Recent advances on the role of G0S2
- PMID: 40679675
- PMCID: PMC12274192
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03198-4
Recent advances on the role of G0S2
Abstract
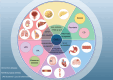
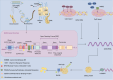
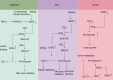
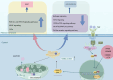
G0S2, formally known as G0/G1 switch gene 2, functions as an inhibitor of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), a key enzyme in lipolysis that hydrolyzes triglycerides (TG) to diacylglycerol and fatty acid (FA). G0S2 can directly interact with ATGL, suppressing its hydrolase activity. Recently, G0S2 has been implicated in immune system abnormalities, chronic inflammation, and tumorigenesis. However, the underlying mechanisms and roles of G0S2 in immune system disorders and cancer remain incompletely understood. In this review, we provide an overview of the current knowledge on G0S2, highlighting its regulation at different levels and unveiling its potential as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in immune-related diseases and cancer. The discussion covers the roles of G0S2 in lipolysis, lipid synthesis, inflammation, and various cancers.
Keywords: Adipose triglyceride lipase; Cancer; G0/G1 switch gene 2; Inflammation; Lipolysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to publish: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lipid Droplets in Cancer| SpringerLink. 2025. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/112_2020_51. Accessed March 24. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous