Use of the Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System Activity Feature Reduces Insulin Delivery and Attenuates the Drop in Glycemia Associated With Exercise in a Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40680105
- PMCID: PMC12368368
- DOI: 10.2337/dc25-0141
Use of the Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System Activity Feature Reduces Insulin Delivery and Attenuates the Drop in Glycemia Associated With Exercise in a Randomized Controlled Trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum. Use of the Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System Activity Feature Reduces Insulin Delivery and Attenuates the Drop in Glycemia Associated With Exercise in a Randomized Controlled Trial Diabetes Care 2025;48:1598-1606.Diabetes Care. 2025 Oct 20:dc26er01a. doi: 10.2337/dc26-er01a. Online ahead of print. Diabetes Care. 2025. PMID: 41115044
Abstract
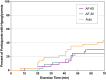
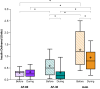
Objective: To compare the efficacy of enabling Activity feature 60 (AF-60) or 30 min (AF-30) before prolonged exercise versus the automated mode (Auto) in adults and adolescents with type 1 diabetes wearing the Omnipod 5 System.
Research design and methods: In this three-way crossover study, 38 participants (age 30 ± 15 years; BMI 24.7 ± 4.1 kg/m2; HbA1c 7.5% ± 0.9% [58 ± 11 mmol/mol]) from the extension phase of the pivotal trial of the Omnipod 5 System completed a 70-min treadmill session at 64-76% maximum heart rate in a postabsorptive state under each of the three conditions. Auto was resumed after exercise, and glycemia and insulin delivery metrics were examined in the 4-h postexercise period.
Results: The percentage of participants who developed hypoglycemia during exercise did not differ significantly between Auto (42%) and AF-60 (29%; P = 0.34) or AF-30 (24%; P = 0.14). However, AF-60 and AF-30 reduced insulin delivery compared with Auto in the hour before (P < 0.001) and during exercise (P < 0.001). There was also a favorable attenuation in glucose drop during exercise when comparing Auto (-57 ± -35 mg/dL) with AF-60 (-44 ± -33 mg/dL; P = 0.02) and AF-30 (-36 ± -34 mg/dL; P = 0.01). In the postexercise period, glycemia and insulin delivery were comparable.
Conclusions: Enabling the Activity feature either 60 or 30 min before exercise reduced insulin delivery and attenuated glucose drops relative to Auto, but hypoglycemia incidence was not different across the three conditions. These findings support the use of the Omnipod 5 System for exercise but highlight the importance of using additional strategies, such as earlier use of Activity feature and/or carbohydrate intake to further reduce hypoglycemia risk.
© 2025 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bohn B, Herbst A, Pfeifer M, et al. ; DPV Initiative. Impact of physical activity on glycemic control and prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in adults with type 1 diabetes: a cross-sectional multicenter study of 18,028 patients. Diabetes Care 2015;38:1536–1543 - PubMed
-
- Johansen RF, Caunt S, Heller S, et al. Factors influencing physical activity level in adults with type 1 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Can J Diabetes 2024;48:431–438.e1 - PubMed

