BLIMP1 negatively regulates IL-2 signaling in T cells
- PMID: 40680114
- PMCID: PMC12273773
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adx8105
BLIMP1 negatively regulates IL-2 signaling in T cells
Abstract
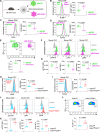
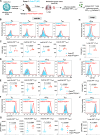
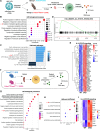
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) regulates immune homeostasis by fine-tuning the balance between effector and regulatory T (Treg) cells. To identify regulators of IL-2 signaling, we performed genome-wide CRISPR-knockout screening in IL-2-dependent cells derived from a patient with adult T cell leukemia (ATL) and found enrichment of single guide RNAs targeting PRDM1, which encodes B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1 (BLIMP1). BLIMP1 inhibits IL-2 production by T cells; however, its role in IL-2 signaling remains unknown. Here, we show that overexpressing Prdm1 down-regulated IL-2 signaling, whereas Prdm1-deficiency enhanced IL-2 signaling in mouse CD4+ T cells and Treg cells with augmented IL-2 signaling in T cells from influenza-infected mice and during adoptive T cell transfer-induced colitis. Deleting PRDM1 in human CD4+ T cells and Treg cells also increased IL-2 signaling. Furthermore, CD4+ T cells from patients with ATL expressed less BLIMP1 and had enhanced IL-2 signaling, whereas overexpressing PRDM1 in ATL cells suppressed IL-2 signaling. Thus, BLIMP1 inhibits IL-2 signaling during normal and pathophysiological responses, suggesting that manipulating BLIMP1 could have therapeutic potential.
Figures




References
-
- Morgan D. A., Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R., Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science 193, 1007–1008 (1976). - PubMed
-
- Kim H. P., Imbert J., Leonard W. J., Both integrated and differential regulation of components of the IL-2/IL-2 receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 17, 349–366 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J., Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature 302, 305–310 (1983). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

