Preclinical assessment of the selective androgen receptor modulator RAD140 to increase muscle mass and bone mineral density
- PMID: 40680216
- PMCID: PMC12274021
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.70463
Preclinical assessment of the selective androgen receptor modulator RAD140 to increase muscle mass and bone mineral density
Abstract
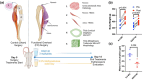
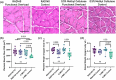
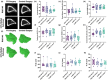
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are important hypertrophic molecules that are potential treatments for many types of myopathy and osteopathy. This study aimed to determine if the SARM RAD140 had additive effects on muscle hypertrophy when combined with the functional overloading (FO) of the plantaris muscle. Male, Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 10 rats/group) were randomly selected into one of four treatment groups: (1) RAD140-FO, (2) RAD140-Control, (3) Vehicle-Control, or (4) Vehicle-FO. RAD140 groups received drugs through drinking water, and control groups received only Vehicle (methylcellulose). Standard rat chow and water were provided ad libitum. Muscle weights of the triceps-surae group and muscle fiber cross-sectional area (CSA) were measured. Muscle weight analysis showed a marked increase in RAD140-FO groups but was not statistically different from the Vehicle-FO group. CSA results indicated similar findings; however, RAD140-Control showed significantly elevated CSA compared to Vehicle-Control. The tibial microarchitecture was analyzed using micro computed tomography. RAD140 did not impact cortical or trabecular bone structural morphometric properties following 14 days of treatment. The data presented here show the potential of RAD140 to stimulate muscle hypertrophy in young healthy rats.
Keywords: RAD140; SARM; cross‐sectional area; functional overload; hypertrophy; skeletal muscle.
© 2025 The Author(s). Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Apr 30;(4):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3:CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. PMID: 23633361 Updated.
-
[Eccentric treadmill exercise promotes adaptive hypertrophy of gastrocnemius in rats].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2025 Jun 25;77(3):449-464. doi: 10.13294/j.aps.2025.0051. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40566712 Chinese.
-
Combination of running and energy restriction impairs bone parameters but does not inhibit endurance adaptations in fast-twitch muscle in young female rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025 Jul 1;139(1):14-26. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00978.2024. Epub 2025 May 23. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025. PMID: 40407828
-
Leptin Enhances M1 Macrophage Polarization and Impairs Tendon-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair: A Rat Model.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 May 1;483(5):939-951. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003428. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39982019
References
-
- Antonio, J. , Wilson, J. D. , & George, F. W. (1999). Effects of castration and androgen treatment on androgen‐receptor levels in rat skeletal muscles. Journal of Applied Physiology (1985), 87(6), 2016–2019. - PubMed
-
- Banu, J. , Wang, L. , & Kalu, D. N. (2003). Effects of increased muscle mass on bone in male mice overexpressing IGF‐I in skeletal muscles. Calcified Tissue International, 73(2), 196–201. - PubMed
-
- Basaria, S. , Collins, L. , Dillon, E. L. , Orwoll, K. , Storer, T. W. , Miciek, R. , Ulloor, J. , Zhang, A. , Eder, R. , Zientek, H. , Gordon, G. , Kazmi, S. , Sheffield‐Moore, M. , & Bhasin, S. (2013). The safety, pharmacokinetics, and effects of LGD‐4033, a novel nonsteroidal oral, selective androgen receptor modulator, in healthy young men. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 68(1), 87–95. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

