Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Trigger and Exacerbate Anti-CV2/CRMP5 Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes
- PMID: 40680246
- PMCID: PMC12275902
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200446
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Trigger and Exacerbate Anti-CV2/CRMP5 Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes
Abstract
Background and objectives: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are oncologic treatments that may trigger or worsen paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes (PNSs). This study describes patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS treated by ICI, compares the post-ICI group with ICI-naïve patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS, and estimates the overall survival of ICI-treated patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS, Hu-PNS, and Ma2-PNS.
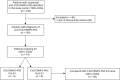
Methods: The medical records of patients positive for anti-CV2/CRMP5 antibodies were retrospectively reviewed at the French Reference Centre to identify those treated with ICI (2016-2024). Patients with a preexisting PNS were described separately from those with post-ICI PNS; the latter were then compared with ICI-naïve patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS diagnosed in the same study period. An overall survival analysis between ICI-treated patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS, Hu-PNS, and Ma2-PNS was performed.
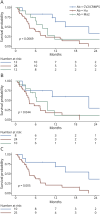
Results: Fourteen patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS treated with ICIs were included. Eight patients [median age, 73 years (range: 60-87); 87.5% men] developed post-ICI PNS after a median of 3.5 ICI cycles (range: 1-7). The frequency and distribution of clinical phenotypes (isolated neuropathy [n = 3] or a multifocal neurologic involvement [encephalopathy, limbic syndrome, brainstem syndrome, cerebellar syndrome, ocular syndrome, neuropathy, and/or dysautonomia; n = 5]) were similar to those of ICI-naïve CV2/CRMP5-PNS (n = 48). The frequency of severe presentations (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] score > 3) at diagnosis was similar between post-ICI patients and ICI-naïve patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS (63% vs 48%, p = 0.7) and slightly higher at last visit in post-ICI patients (88% vs 54%, p = 0.12). Anti-CV2/CRMP5 antibodies were undetectable in the only patient with a pre-ICI serum sample. Among the 6 patients with preexisting CV2/CRMP5-PNS [median age, 66 years (range: 54-79); 50% men] who received ICIs, PNS symptoms worsened in 5 (83%) [median mRS increase of 1.5 points (range: 1-3)]. The median overall survival (22 months) was significantly longer in the ICI-treated patients with CV2/CRMP5-PNS compared with the Hu-PNS and Ma2-PNS groups (4 months and 8 months, respectively, p = 0.0069).
Discussion: ICIs may trigger the onset and exacerbate the progression of CV2/CRMP5-PNS. Post-ICI forms are clinically undistinguishable but possibly more severe than their ICI-naïve counterparts. Increased surveillance is needed in identifying preexisting PNSs, with extreme caution when considering ICI treatment. Post-ICI-induced PNSs have variable prognosis according to the associated onconeural autoantibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
