Viral mitochondriopathy in COVID-19
- PMID: 40680383
- PMCID: PMC12284291
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103766
Viral mitochondriopathy in COVID-19
Abstract
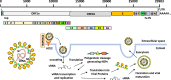
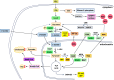
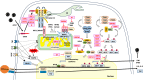
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), disrupts cellular mitochondria, leading to widespread chronic inflammation and multi-organ dysfunction. Viral proteins cause mitochondrial bioenergetic collapse, disrupt mitochondrial dynamics, and impair ionic homeostasis, while avoiding antiviral defenses, including mitochondrial antiviral signaling. These changes drive both acute COVID-19 and its longer-term effects, known as "long COVID". This review examines new findings on the mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 affects mitochondria and for the impact on chronic immunity, long-term health risks, and potential treatments.
Keywords: Chronic inflammation; Exacerbation; Long COVID; Mitochondria; Mitochondrial antiviral signaling pathway; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Berlin D.A., Gulick R.M., Martinez F.J. Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383(25):2451–2460. - PubMed
-
- Xia C.Y., Niu M.M., Hu P. More on SARS-CoV-2 variants and pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023;389(3):287. - PubMed
-
- Kesheh M.M., Hosseini P., Soltani S., Zandi M. An overview on the seven pathogenic human coronaviruses. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022;32(2) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

