The potassium channel K2P2.1 shapes the morphology and function of brain endothelial cells via actin network remodeling
- PMID: 40681505
- PMCID: PMC12274505
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61816-9
The potassium channel K2P2.1 shapes the morphology and function of brain endothelial cells via actin network remodeling
Abstract
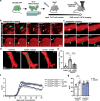
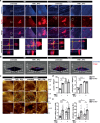
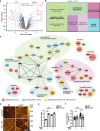
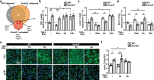
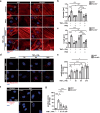
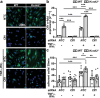
K2P2.1 (gene: Kcnk2), a two-pore-domain potassium channel, regulates leukocyte transmigration across the blood-brain barrier by a yet unknown mechanism. We demonstrate that Kcnk2-/- mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells (MBMECs) exhibit an altered cytoskeletal structure and surface morphology with increased formation of membrane protrusions. Cell adhesion molecules cluster on those protrusions and facilitate leukocyte adhesion and migration in vitro and in vivo. We observe downregulation of K2P2.1 and activation of actin modulating proteins (cofilin 1, Arp2/3) in inflamed wildtype MBMECs. In the mechanosensitive conformation, K2P2.1 shields the phospholipid PI(4,5)P2 from interaction with other actin regulatory proteins, especially cofilin 1. Consequently, after stimulus-related K2P2.1 downregulation and dislocation from PI(4,5)P2, actin rearrangements are induced. Thus, K2P2.1-mediated regulatory processes are essential for actin dynamics, fast, reversible, and pharmacologically targetable.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bittner, S. et al. Endothelial TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (TREK1) regulates immune-cell trafficking into the CNS. Nat. Med.19, 1161–1165 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Honoré, E. The neuronal background K2P channels: focus on TREK1. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.8, 251–261 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Vestweber, D. How leukocytes cross the vascular endothelium. Nat. Rev. Immunol.15, 692–704 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 549557400/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 417677437/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- INST 392/141-1 FUGG/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- KU 1496/7-3/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- KU 1496/7-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

