Traversing the Valley of Death for nanotechnology-based natural products: strategies and insights from pharmaceutical stakeholders
- PMID: 40681832
- PMCID: PMC12508012
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-025-01923-8
Traversing the Valley of Death for nanotechnology-based natural products: strategies and insights from pharmaceutical stakeholders
Abstract
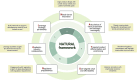
Nanotechnology-based natural products hold significant therapeutic promise by improving the bioavailability and efficacy of natural products. However, their translation from laboratory to clinic remains hindered by a complex interplay of strategic misalignment, regulatory complexity, and organisational hurdles, often leading to failure in the so-called “Valley of Death”. To understand the drivers of successful translation and commercialisation, this study engaged 16 pharmaceutical stakeholders through semi-structured, in-depth interviews. Thematic analysis revealed three critical enablers. First, product-market fit requires early integration of market analysis and need-driven innovation to ensure alignment with unmet medical needs and commercial viability. Moreover, effective articulation of value propositions is essential to translate technical performance into perceived value for both investors and end-users. Second, product differentiation and positioning are essential to communicate competitive advantage in a crowded and cost-sensitive market. Strategic use of comparators, value metrics, and strategic messaging are critical to demonstrate tangible benefits over existing formulations, while avoiding unnecessary complexity to preserve affordability. Third, cross-sector and horizontal collaborative networks across academia, industry, regulators, manufacturers, and peer companies play a vital role in overcoming translational challenges by fostering regulatory preparedness and pooling complementary expertise and resources. Building on these findings, we propose the NATURAL framework as a translational planning tool to support early decision-making by helping innovators anticipate key barriers, align strategies, and improve the likelihood of clinical translation. Altogether, this study offers actionable insights and a structured planning tool to de-risk and accelerate the translation of nano-based natural products from bench to market.
Keywords: Commercialisation; Nanotechnology; Natural products; Pharmaceutical innovation; Translational framework; Valley of Death.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: This study was conducted in accordance with the National Statement on Ethical Conduct in Human Research. Approved was granted by the Monash University Human Research Ethics Committee (Project ID: 27759). Consent to participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Competing Interests: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- The Nanodatabase. Consumer Products. https://nanodb.dk/en/analysis/consumer-products (2024). Accessed 11 June 2025 2025.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources