Myc overexpression improves recovery from myocardial infarction associated with cardiomyocyte hyperplasia in the mouse heart
- PMID: 40681845
- PMCID: PMC12274510
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08360-w
Myc overexpression improves recovery from myocardial infarction associated with cardiomyocyte hyperplasia in the mouse heart
Abstract
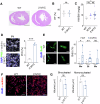
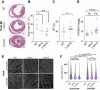
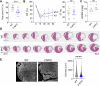
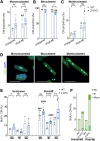
Adult mammalian hearts lack the ability to regenerate after a myocardial infarction, which leads to heart failure progression. Therefore, finding ways to promote regeneration is a major goal in the development of cardiovascular therapies. In this study, we focus on the role of Myc moderate overexpression in response to acute ischemic injury. We have previously shown that moderate Myc overexpression is not detrimental to cardiac function and promotes cell competition and a hyperplastic phenotype. Here, we describe that Myc overexpression in non-regenerative postnatal hearts promotes functional improvements and reduced scar formation after myocardial infarction. This response correlates with a hyperplastic phenotype in postnatal and adult hearts, characterized by bigger hearts, smaller cardiomyocyte size and increased BrdU incorporation without ploidy increase. Moreover, we show that Myc strongly enhances diploid cardiomyocyte proliferation and the generation of new binucleated cardiomyocytes. Thus, Myc promotes functional and morphological improvements in the heart following acute ischemia and this response correlates with promotion of hyperplasia versus hypertrophy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests
Figures
References
-
- Jessup, M. et al. 2009 focused update: ACCF/AHA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure in Adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines: developed in collaboration with the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. Circulation,119, 1977–2016 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Soonpaa, M. H. et al. Cardiomyocyte DNA synthesis and binucleation during murine development. Am. J. Physiol.2712, H2183–H2189 (1996). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SC1-BHC-07-2019. Ref. 874764 "REANIMA"/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 European Institute of Innovation and Technology (H2020 The European Institute of Innovation and Technology)
- TNE-17CVD04/Fondation Leducq
- AdG REACTIVA Ref. 101142005/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 Ideas: European Research Council (FP7-IDEAS-ERC - Specific Programme: "Ideas" Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
- LCF/BQ/DR22/11950017/"la Caixa" Foundation (Caixa Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

