Central and peripheral arterial stiffness and sarcopenia in hospitalized older adults
- PMID: 40682736
- PMCID: PMC12276136
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-025-03122-4
Central and peripheral arterial stiffness and sarcopenia in hospitalized older adults
Abstract
Objective: Both sarcopenia and arterial wall stiffening are frequent findings among hospitalized older adults, and further insight should be gained to explore their pathophysiological mechanisms and possible correlations.
Methods: 90 hospitalized geriatric patients (mean age 83.94 ± 6.6 years, 38.89% female, 36.7% sarcopenic) have been enrolled, and underwent clinical, comorbidity and biochemical assessment. Sarcopenia was investigated following the diagnostic algorithm according to European guidelines assessing muscular strength, using a portable dynamometer, and muscle mass by bio-impedance analysis (BIA); carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV), carotid-radial PWV (crPWV), femoral-pedal PWV (fpPWV) and cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) were obtained for each.
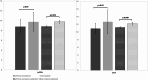
Results: Sarcopenic patients (n = 33) were older (p < 0.01) than subjects without sarcopenia (n = 57). Sarcopenic patients presented higher CAVI (12.67 ± 3.12 vs. 10.91 ± 1.4, p < 0.01) and fpPWV, but not cfPWV and crPWV. In backward analysis muscle strength and comorbidity index resulted good indipendent variables of fpPWV (R2 0.11), muscle strength, comorbidity index and sex could predict CAVI (R2 0.22). When examining sarcopenia diagnoses determinants, in a logistic binary regression model and considering several possible covariates, fpPWV resulted a significant indipendent variable of sarcopenia along with age and sex.
Conclusion: increased indexes of arterial stiffness are shown in sarcopenic hospitalized older adults as compared to hospitalized patients without sarcopenia; peripheral arterial segments of the lower limb appeared to be more involved in the stiffening process, as compared to central segments.
Keywords: Arterial stiffness; Cardio-ankle vascular index; Femoral-pedal pulse wave velocity; Peripheral arterial stiffness; Sarcopenia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chhetri JK, de Souto Barreto P, Fougère B, Rolland Y, Vellas B, Cesari M (2018) Chronic inflammation and sarcopenia: A regenerative cell therapy perspective. Exp Gerontol 103:115–123 - PubMed
-
- Hingorani AD, Cross J, Kharbanda RK, Mullen MJ, Bhagat K, Taylor M et al (2000) Acute systemic inflammation impairs endothelium-dependent dilatation in humans. Circulation 102:994–999 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

