High expression of eIF4A1 promotes angiogenesis through the NF‑κB/VEGFA pathway and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer
- PMID: 40682841
- PMCID: PMC12308842
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2025.8951
High expression of eIF4A1 promotes angiogenesis through the NF‑κB/VEGFA pathway and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer
Abstract
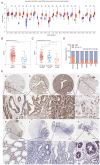
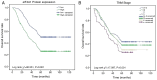
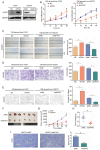
Increased eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A (eIF4A1) expression is observed in numerous types of cancer and is associated with carcinogenesis; however, little is known about the role of eIF4A1 in gastric cancer (GC) angiogenesis. In the present study, a total of 1,758 gastric mucosa samples were collected for immunohistochemical staining in tissue microarrays. The expression levels of eIF4A1 and their association with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis were analyzed using χ2 test and univariate/multivariate analysis. The effects of abnormal eIF4A1 expression in GC cells on proangiogenic activity was detected using the Cell Counting Kit‑8 proliferation assay, wound healing assay, Transwell assay, angiogenesis assay and a subcutaneous tumor model. The role of eIF4A1 in tumor‑infiltrating lymphocytes was explored using bioinformatics analysis. Furthermore, the effect of eIF4A1 on proangiogenic factors was confirmed by the quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. Notably, eIF4A1 was highly expressed in GC tissues, and was associated with patient age, tumor differentiation, depth of invasion, distant metastasis and Tumor‑Node‑Metastasis stage. Furthermore, it was suggested that high eIF4A1 expression could be regarded as a poor prognostic biomarker for patients with GC. The expression levels of eIF4A1 in GC cells were also positively related to proliferation, migration and the tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and microvessel density in vivo. Furthermore, eIF4A1 in GC cells regulated the infiltration of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, and promoted the expression of VEGFA and NF‑κB. In conclusion, eIF4A1 may promote GC angiogenesis through the NF‑κB/VEGFA pathway, and could be considered an independent prognostic biomarker for patients with GC.
Keywords: NF‑κB; VEGFA; angiogenesis; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A; gastric cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Li ZY, Liu K, Zhang WH. Epidemiologic features and trends of gastric cancer in the world and China:interpretation of the GLOBOCAN 2018–2022. https://www.gensurg.cn/article/10.7507/1007-9424.202409074 Chin J Bases Clin Gen Surg. 2024;31:1236–1245.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

