Plasma proteomics for biomarker discovery in childhood tuberculosis
- PMID: 40683862
- PMCID: PMC12276249
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61515-5
Plasma proteomics for biomarker discovery in childhood tuberculosis
Abstract
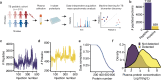
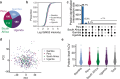
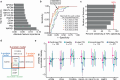
Failure to rapidly diagnose tuberculosis disease (TB) and initiate treatment is a driving factor of TB as a leading cause of death in children. Current TB diagnostic assays have poor performance in children, thus a global priority is the identification of novel non-sputum-based TB biomarkers. Here we use high-throughput proteomics to measure the plasma proteome for 511 children, with and without HIV, and across 4 countries, to distinguish TB status using standardized definitions. By employing a machine learning approach, we derive four parsimonious biosignatures encompassing 3 to 6 proteins that achieve AUCs of 0.87-0.88 and which all reach the minimum WHO target product profile accuracy thresholds for a TB screening test. This work provides insights into the unique host response in pediatric TB disease, as well as a non-sputum biosignature that could reduce delays in TB diagnosis and improve the detection and management of TB in children worldwide.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Plasma proteomics for novel biomarker discovery in childhood tuberculosis.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 20:2024.12.05.24318340. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.05.24318340. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 19;16(1):6657. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61515-5. PMID: 39677468 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024 (World Health Organization, Genève, Switzerland, 2024).
-
- World Health Organization & Viney, K. Roadmap Towards Ending TB in Children and Adolescents (World Health Organization, Genève, Switzerland, 2023).
-
- MacLean, E. et al. A systematic review of biomarkers to detect active tuberculosis. Nat. Microbiol.4, 748–758 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 AI144040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI175312/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI109755/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- L30 AI126532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23HL153581/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01AI175312/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01AI152161/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- K23AI144040/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- P30 AI168386/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI152161/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI182244/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

