Pre-transplant predictors of 3-Month survival following liver transplantation for acute liver failure in adult and pediatric patients in Türkiye
- PMID: 40683961
- PMCID: PMC12276286
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11298-y
Pre-transplant predictors of 3-Month survival following liver transplantation for acute liver failure in adult and pediatric patients in Türkiye
Abstract
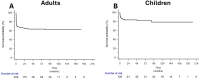
This multicenter retrospective study analyzed 336 patients (236 adults, 100 children) who underwent liver transplantation (LT) for acute liver failure (ALF) between 2002 and 2019 across 14 centers in Türkiye. The aim was to evaluate pretransplant factors influencing short-term posttransplant survival. Median MELD and PELD scores were 31 and 30, respectively. The most common ALF etiologies were viral, indeterminate, and drug-induced causes. Living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) was more common in children (86.0%) than adults (57.2%). Mean posttransplant survival was 166±9 months in children and 117±6 months in adults. In adults, LDLT significantly improved survival compared to deceased donor LT (DDLT), with survival of 135 vs. 89 months (p=0.0012). Although pediatric LDLT recipients had longer mean survival than DDLT recipients (167 vs. 132 months), this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.5959). Three-month mortality was associated with low albumin and grade 4 hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in children. In adults, independent predictors of early mortality included DDLT, serum sodium >140 mEq/L, MELD >35, pH <7.3, and grade 4 HE. Our data suggest that LDLT may offer a survival advantage, particularly in adults with ALF. Identifying pretransplant risk factors is essential for improving early outcomes and guiding clinical decision-making.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Liver transplantation; Living donor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Grants and financial support: The authors received no funding for this work.
Figures


References
-
- Wlodzimirow, K. A., Eslami, S., Abu-Hanna, A., Nieuwoudt, M. & Chamuleau, R. A. Systematic review: acute liver failure - one disease, more than 40 definitions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.35 (11), 1245–1256 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Lee, W. M. Acute liver failure. N Engl. J. Med.329 (25), 1862–1872 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Wendon, J. et al. EASL clinical practical guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J. Hepatol.66 (5), 1047–1081 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Jayalakshmi, V. T. & Bernal, W. Update on the management of acute liver failure. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care. 26 (2), 163–170 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

