The influence of metformin treatment on the circulating proteome
- PMID: 40684475
- PMCID: PMC12301841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105859
The influence of metformin treatment on the circulating proteome
Abstract
Background: Metformin is one of the most used drugs worldwide. Given the increasing use of proteomics in trials, bioresources, and clinics, it is crucial to understand the influence of metformin on the levels of the circulating proteome.
Methods: We analysed a combined longitudinal proteomics dataset from the IMPOCT, RAMP and S3WP-T2D clinical trials in 98 participants before and after metformin exposure. This discovery analysis contained 372 proteins measured by proximity extension assays (Olink). We followed up experiment-wise statistically significant findings in two cross-sectional cohorts of people with type 2 diabetes comparing metformin treated and untreated individuals: IMI-DIRECT (784 participants, 372 proteins, Olink) and IMI-RHAPSODY (1175 participants, 1195 proteins, SomaLogic).
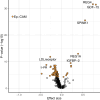
Findings: Overall, 23 protein analytes were robustly associated with exposure to metformin in the discovery and replication. This includes 11 protein-metformin associations that replicated in both replication sets and platforms (REG4, GDF15, REG1A, t-PA, TFF3, CDH5, CNTN1, OMD, NOTCH3, THBS4 and CD93), with the remaining 12 protein-metformin associations replicated using the Olink platform (EPCAM, SPINK1, SAA-4, COMP, ITGB2, ADGRG2, FAM3C, MERTK, COL1A1, HAOX1, VCAN, TIMD4) but not measured on the SomaLogic platform. Gene-set enrichment analysis revealed that the metformin exposure was associated with intestinal associated proteins.
Interpretation: These data highlight the need to account for exposure to metformin, and potentially other drugs, in proteomic studies and where protein biomarkers are used for clinical care.
Funding: Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertaking 2, under grant agreement no. 115881 (RHAPSODY) and the Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertaking under grant agreement no. 115317 (DIRECT), resources of which are composed of financial contribution from the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) and EFPIA companies in kind contribution as well as the Swiss State Secretariat for Education Research' and Innovation (SERI), under contract no. 16.0097 (RHAPSODY).
Keywords: Biomarker; Metformin; Proteomics; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests JS received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Luminex and Olink. RWK is currently an employee of Novo Nordisk A/S and owns stock of Novo Nordisk A/S. There are no other relevant conflicts of interest to disclose for this study.
Figures

References
-
- Gerstein H.C., Pare G., Hess S., et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 as a novel biomarker for metformin. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(2):280–283. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

