Implementing heart failure disease management in primary care: a mixed-methods analysis of the IMPACT-B study
- PMID: 40685241
- PMCID: PMC12278146
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093414
Implementing heart failure disease management in primary care: a mixed-methods analysis of the IMPACT-B study
Abstract
Objectives: Heart failure is an important health problem and patients are generally older with several comorbidities. Multidisciplinary heart failure care is therefore recommended. However, there is little evidence in real-world settings on how to involve primary care health professionals and how to evaluate such programmes. The main objective of this study is to integrate and evaluate several disease management interventions in a primary care setting.
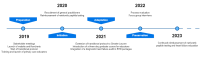
Design: Prospective, non-randomised, observational implementation study with a mixed-methods process evaluation conducted over 3 years (2020-2022).
Setting: Primary care practices and two regional hospitals (one tertiary, one secondary) in the Leuven region, Belgium, serving approximately 100 000 inhabitants.
Participants: 100 general practitioners (GPs) from 19 practices participated. A total of 96 patients were included in the disease management programme. Inclusion criteria for patients included high-risk status for heart failure (HF) readmission, based on clinical criteria. Exclusion criteria were not explicitly defined but participation required informed consent.
Interventions: Four interventions were implemented: (1) online HF education for GPs, (2) reimbursed natriuretic peptide (NP) testing, (3) patient education by trained primary care HF educators and (4) a structured transitional care protocol posthospital discharge.
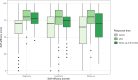
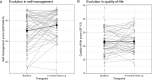
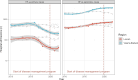
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Primary outcomes included GP self-efficacy in HF management, NP testing rates, HF registration in electronic health records and patient self-efficacy (9-item European Heart Failure Self-Care Behaviour Scale (EHFScB-9)). Secondary outcomes included patient quality of life (Short Form-12 questionnaire (SF-12)), hospital readmission rates and provider satisfaction.
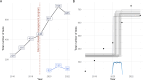
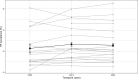
Results: GPs felt more competent in the management of HF after an online education (eight point increase in self-efficacy score after 6 months follow-up, (CI 2.9 to 13, p<0.001)). GPs conducted 314 reimbursed NP tests, half of which scored above age-specific thresholds for referral. After initiation, there was a significant increase in NP testing (Bayes Factor 64), with a total rate of 5.4 tests per 1000 patient years. The proportion of registered HF in patients aged 40 years or older in GPs' electronic health records increased from 2.27% to 2.57% between 2020 and 2022. 96 patients were included in the disease management programme, 75% of these inclusions followed the transitional protocol after discharge for HF. There was significant improvement in patients' self-efficacy after 6-month follow-up (an EHFScB-9 score change of 2.7 points, 95% CI 0.62 to 4.8), but no significant change in quality of life (an SF-12 score change of 0.15 points, 95% CI -1.1 to 1.4). Adherence to the transitional protocol depended on the presence of a specialist HF nurse during admission, 84% of all patients were seen within 14 days after discharge by their general practitioner. Time-trend analysis revealed an increase of HF as a secondary rather than primary cause of admission. Participating healthcare professionals reported satisfaction with the programme.
Conclusions: The IMPACT-B study demonstrated that an integrated disease management programme for HF could be implemented and assessed in routine clinical practice. The programme resulted in increased awareness and registration of HF in primary care, increased self-management of patients and improved follow-up after discharge, although these results should be interpreted cautiously given the uncontrolled pre-post study design.
Trial registration: Trial registration NCT04334447 (clinicaltrials.gov).
Keywords: Aged; Heart failure; Organisation of health services; Primary Health Care; Self-Management.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: WR and MS report no conflict of interest. BV is holder of a chair in Population Health Management at the University of Leuven financed by Novartis, for which GVP and MVdP are co-chair. SJ is holder of a named chair in Cardiology at the University of Leuven financed by AstraZeneca.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Exercise interventions and patient beliefs for people with hip, knee or hip and knee osteoarthritis: a mixed methods review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 17;4(4):CD010842. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010842.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29664187 Free PMC article.
-
Supported self-management for patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): an evidence synthesis and economic analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2015 May;19(36):1-516. doi: 10.3310/hta19360. Health Technol Assess. 2015. PMID: 25980984 Free PMC article.
-
Transition of care for adolescents from paediatric services to adult health services.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 29;4(4):CD009794. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009794.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27128768 Free PMC article.
-
Personalised care planning for adults with chronic or long-term health conditions.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Mar 3;2015(3):CD010523. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010523.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25733495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3599–726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368. - DOI - PubMed
-
- NICE Overview | Chronic heart failure in adults: diagnosis and management | Guidance. 2018. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng106 Available. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145:e895–1032. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001063. - DOI - PubMed
-
- HFPN . Heart failure policy and practice in Europe. London: 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
