A predictive serum miRNA signature impacts diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell viability via inhibition of EGLN1 and TXNRD1 regulators of ferroptosis
- PMID: 40685776
- PMCID: PMC12436215
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.70017
A predictive serum miRNA signature impacts diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell viability via inhibition of EGLN1 and TXNRD1 regulators of ferroptosis
Abstract
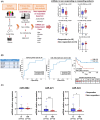
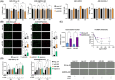
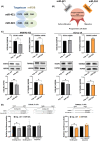
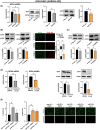
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a heterogeneous disorder. Prognostic factors include genomic alterations and cell-of-origin (COO) subtypes, even though they cannot fully predict treatment response. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) deregulated in patient tumours and blood are promising non-invasive biomarkers. Several circulating miRNAs were found to be correlated with progression-free survival (PFS), independently of other prognosticators. However, miRNA signatures, rather than individual miRNAs, represent more reliable biomarkers and a better mirror of the disease. In this study, we identified circulating miRNAs differentially expressed between R-CHOP refractory and responding subjects by small-RNA sequencing on serum from 33 DLBCL patients. Among the identified miRNAs, the combined expression of three of them improved the predictive performance and was correlated with PFS. Two out of three miRNAs, miR-421 and miR-324-5p, were also differentially expressed in tumour tissues based on treatment response. Overexpressing these miRNAs reduced cell proliferation, viability and resistance to R-CHOP in the germinal centre B-like COO subtype. EGLN1 and TXNRD1, regulators of oxygen metabolism and redox homeostasis, were identified as miRNA targets and the silencing or inhibition of these genes impaired cell viability and induced ferroptosis. These results support the application of a two-miRNA signature and its targets for novel combined therapeutic interventions in DLBCL.
Keywords: circulating microRNAs; diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma; ferroptosis regulators; predictive biomarkers.
© 2025 The Author(s). British Journal of Haematology published by British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures
References
-
- Hill BT, Kahl B. Upfront therapy for diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma: looking beyond R‐CHOP. Expert Rev Hematol. 2022;15(9):805–812. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Mouliere F, Pegtel DM, Chamuleau MED. Turning the tide in aggressive lymphoma: liquid biopsy for risk‐adapted treatment strategies. Trends Mol Med. 2024;30(7):660–672. - PubMed
-
- Lavacchi D, Landini I, Perrone G, Roviello G, Mini E, Nobili S. Pharmacogenetics in diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma treated with R‐CHOP: still an unmet challenge. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;229:107924. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

