Extracellular LCN2 Binding to 24p3R in Astrocytes Impedes α-Synuclein Endocytosis in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 40686313
- PMCID: PMC12533313
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202501694
Extracellular LCN2 Binding to 24p3R in Astrocytes Impedes α-Synuclein Endocytosis in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
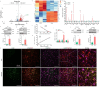
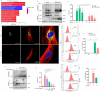
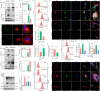
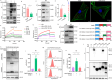
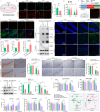
The spread or transmission of pathologic α-synuclein (α-Syn) is emerging as potentially important driver of Parkinson's disease (PD) pathogenesis. Emerging evidence suggests that astrocytes play an important role in uptake/clearance of extracellular α-Syn. However, underlying mechanisms and molecular entities responsible for uptake/clearance of extracellular α-Syn by astrocytes are not known. Here, it is shown that lipocalin-2 (LCN2) is upregulated in astrocytes of MPTP-treated mice by RNA-Seq analysis and positively correlates with pathologic α-Syn level in α-Syn PFF model. Strikingly, deletion of astrocytic LCN2 significantly prevents the pathologic α-Syn accumulation and neurodegeneration. Moreover, 24p3R as a crucial receptor of α-Syn uptake by astrocytes is identified, as well as an important mediator of α-Syn spread in the brain. 24p3R specifically binds to α-Syn and then mediates α-Syn uptake. LCN2 prevents astrocytic uptake of α-Syn by impeding the binding of 24p3R and α-Syn. The identification of LCN2/24p3R as a key regulator of α-Syn by astrocytes provides a new target for the treatment of PD and related α-synucleinopathies.
Keywords: 24p3R; Parkinson's disease; astrocytes; lipocalin‐2; α‐synuclein.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- a) Mao X., Ou M. T., Karuppagounder S. S., Kam T. I., Yin X., Xiong Y., Ge P., Umanah G. E., Brahmachari S., Shin J. H., Kang H. C., Zhang J., Xu J., Chen R., Park H., Andrabi S. A., Kang S. U., Goncalves R. A., Liang Y., Zhang S., Qi C., Lam S., Keiler J. A., Tyson J., Kim D., Panicker N., Yun S. P., Workman C. J., Vignali D. A., Dawson V. L., et al., Science 2016, 353, aah3374; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Chavarria C., Ivagnes R., Souza J. M., Biomolecules 2022, 12, 655. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Chen K., Martens Y. A., Meneses A., Ryu D. H., Lu W., Raulin A. C., Li F., Zhao J., Chen Y., Jin Y., Linares C., Goodwin M., Li Y., Liu C. C., Kanekiyo T., Holtzman D. M., Golde T. E., Bu G., Zhao N., Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 57; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Neupane S., De Cecco E., Aguzzi A., J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 167930. - PubMed
-
- a) Dutta D., Jana M., Majumder M., Mondal S., Roy A., Pahan K., Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5382; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Filippini A., Mutti V., Faustini G., Longhena F., Ramazzina I., Rizzi F., Kaganovich A., Roosen D. A., Landeck N., Duffy M., Tessari I., Bono F., Fiorentini C., Greggio E., Bubacco L., Bellucci A., Missale M., Cookson M. R., Gennarelli M., Russo I., Glia 2021, 69, 681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Yuan J., Liu H., Zhang H., Wang T., Zheng Q., Li Z., Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2108435; - PubMed
- b) Scheiblich H., Dansokho C., Mercan D., Schmidt S. V., Bousset L., Wischhof L., Eikens F., Odainic A., Spitzer J., Griep A., Schwartz S., Bano D., Latz E., Melki R., Heneka M. T., Cell 2021, 184, 5089. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82373851/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82273906/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173797/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- KF-202502/Open fund of State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Nanjing University, China
- 2022YFE0108600/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
