Molecular docking and in vitro anticancer evaluation of potential compounds derived from Indonesian sponge Agelas nakamurai
- PMID: 40686354
- PMCID: PMC12370229
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_701_24
Molecular docking and in vitro anticancer evaluation of potential compounds derived from Indonesian sponge Agelas nakamurai
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluated the anticancer activity (in silico and in vitro) of compounds derived from the Agelas nakamurai collected from Indonesian waters against the triple-negative breast cancer cancer cell line MDA-MB-231.
Background: The marine sponge genus Agelas is known to biosynthesize a variety of secondary metabolites with anticancer properties.
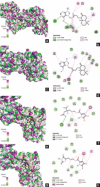
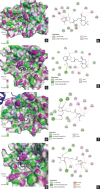
Materials and methods: The compounds were separated using open column and preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. The liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance data were used to characterize compounds. Antiproliferation test of isolated compounds was conducted against the MDA-MB-231 cell line. Meanwhile p53 MDM2 protein [PDB]: 4OQ3, and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (EGFR) protein (PDB: 1T46) were utilized for molecular docking and dynamic (MD) analysis.
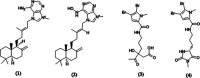
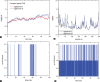
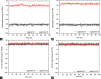
Results: LC-MS data of fraction F7 indicated the presence of agelasine D, ageloxime D, agelanin B, and midpacamide. Further purification of fraction F7 led to the agelasin D and ageloxime D. Both compounds inhibited the MDA-MB-231 cell line with IC50 values of 7.09 and 171.07 µM, respectively. The docking results showed that the binding affinity of agelasine D and ageloxime D to 4OQ3 and 1T46 were close, with scores ranging from -7.3 to -9.0 kcal/mol. MD simulation within 100 ns indicated agelasin D and ageloxime-D make stable binding to the targeted proteins with root-mean-square deviation <2Å.
Conclusions: The isolated compounds from A. nakamurai showed potent against the MDA-MB-231 cell line, based on in vitro and in silico analysis. The MD data supported that the compounds effectively inhibit cancer growth through the MDM2 or EGFR pathways. Thus, this study suggested further in vitro mechanism of action analysis.
Keywords: Agelasine D; ageloxime D; triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Indian Journal of Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficient Synthesis, Anticancer Evaluation of Triazole-Thiadiazole/Benzo[d]Oxazole Scaffolds, and Investigation of Their Reactivity Properties Using Density-Functional Theory Calculations and In Silico Docking.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Jul;22(7):e202402470. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202402470. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39972950
-
Exploitation of novel pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine scaffold tethered to thiazole as potential EGFR/HER2 dual kinase inhibitor to overcome lapatinib resistant breast cancer: Design, synthesis, in silico docking and molecular dynamic simulation.Bioorg Chem. 2025 Aug;163:108671. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108671. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Bioorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 40480106
-
Novel benzenesulfonamides as dual VEGFR2/FGFR1 inhibitors targeting breast cancer: Design, synthesis, anticancer activity and in silico studies.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Nov;152:107728. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107728. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39178704
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Platinum-containing regimens for metastatic breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 23;6(6):CD003374. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003374.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28643430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu CW, Chiang L, Chao CH, Huang YL, Chiou SF, Wang LC, et al. Nakamusines A − C, new 9-methyladeninium diterpenoid alkaloids from a Formosan marine sponge Agelas nakamurai. Tetrahedron. 2023;149:133745.
-
- Fu CW, Lin YC, Chiou SF, Huang TY, Yang YJ, Wu SH, et al. 2-guanidinoethanesulfonyl sesquiterpenes from the marine sponge Agelas nakamurai. Tetrahedron Lett. 2022;103:153964.
-
- Murniasih T, Hadi TA, Ahmadi P, Sari M, Bustanussalam B, Hadisaputri YE, et al. Assessments of anti-breast cancer activity and profiling of active compounds using LC-MS/MS from the Indonesian Agelas nakamurai. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2024;14:204–9.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

