Human oral pharmacokinetics of 4-hydroxy isoleucine and dosage simulation studies for predicting its pharmacodynamics in diabetes
- PMID: 40686357
- PMCID: PMC12370230
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_736_23
Human oral pharmacokinetics of 4-hydroxy isoleucine and dosage simulation studies for predicting its pharmacodynamics in diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: 4-hydroxy isoleucine (4-HIL), a potent glucose-lowering agent and insulin secretagogue, is widely available in nutraceutical market as fenugreek seed extract formulations. This study aims to elucidate the oral pharmacokinetics (PK) of 4-HIL in healthy human volunteers to standardize its dose and dosing regimen, ensuring its potential for effective diabetes management.
Methodology: Twelve healthy volunteers received a single oral administration of 150 mg of 4-HIL as fenugreek seed extract tablets. Caplillary blood samples were collected at various time points within 24 h and plasma levels of 4-HIL were quantified using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In vitro studies on 4-HIL pharmacodynamics, derived from the literature, were used to calculate the half-minimal effective concentration (EC50). PK assessments based on compartmental modelling and dosage simulation studies were conducted using PKsolver and ModVizPOP, respectively. The PK simulation included three distinct dosage regimens (150 mg thrice daily, 225 mg twice daily, or 450 mg once daily) to evaluate EC50 level attainment.
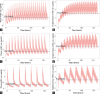
Results: The best-fit was observed with a two-compartmental model, with maximum 4-HIL plasma concentration (Concentration maximum, 2.42 ± 0.61 µg/mL) observed at 0.5 h (Time maximum). The derived mean EC50 of 4-HIL, needed to reduce blood glucose, was 1.50 ± 0.31 µg/mL. The PK simulation study indicated that daily intake of 450 mg 4-HIL in all three tested dosing regimens had maintained EC50 levels more than 18 h for glucose-lowering effects.
Conclusion: The optimal 4-HIL dose of 450 mg/day up to three divided dosing regimens has proven effective and hence may be considered for future diabetic trials.
Keywords: 4-hydroxy isoleucine; diabetes; dosing regimen; fenugreek; pharmacokinetics; simulation.
Copyright © 2025 Indian Journal of Pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Jetté L, Harvey L, Eugeni K, Levens N. 4-hydroxyisoleucine: A plant-derived treatment for metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10:353–8. - PubMed
-
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and kidney diseases; Bethesda, Maryland, USA: 2012. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. - PubMed
-
- Middha SK, Bhattacharjee B, Saini D, Baliga MS, Nagaveni MB, Usha T. Protective role of Trigonella foenum graceum extract against oxidative stress in hyperglycemic rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011;15:427–35. - PubMed
-
- Hamza N, Berke B, Cheze C, Le Garrec R, Umar A, Agli AN, et al. Preventive and curative effect of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. seeds in C57BL/6J models of type 2 diabetes induced by high-fat diet. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;142:516–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

