The anti-aging Klotho protects glioblastoma macrophages from radiotherapy-induced inflammation and predicts immunotherapy response
- PMID: 40686387
- PMCID: PMC12439078
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.70038
The anti-aging Klotho protects glioblastoma macrophages from radiotherapy-induced inflammation and predicts immunotherapy response
Abstract
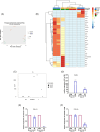
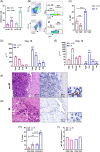
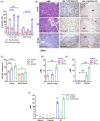
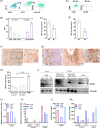
Immunosuppressive myeloid cells, such as microglia and macrophages, play a key role in mediating resistance to immunotherapy in glioblastoma patients. Bulk RNA sequencing analysis revealed elevated expression of Klotho (Kl) in gliomas derived from irradiated glioma-bearing mice. Klotho, which encodes an anti-aging protein, was found to be upregulated in glioma-associated microglia/macrophages (GAMs) exhibiting an M1 pro-inflammatory phenotype. This upregulation appeared to enhance the antitumor efficacy of a combination of radiotherapy and dendritic cell (DC) immunotherapy. Furthermore, transcript levels of KL in tumor specimens and corresponding serum levels in glioblastoma patients undergoing DC immunotherapy were correlated with favorable prognostic outcomes and improved treatment responses. Given its expression in human M1-like GAMs, serum KL levels can offer valuable insights into the immune microenvironment and hold clinical significance as a peripheral biomarker. These findings highlight the pivotal role of Klotho as a prognostic biomarker for predicting responses to immunotherapy, with potential applications for monitoring tumor progression or regression through changes in serum levels.
Keywords: glioblastoma; immunotherapy; inflammation; macrophages; radiotherapy.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987‐996. - PubMed
-
- Pombo Antunes AR, Scheyltjens I, Lodi F, et al. Single‐cell profiling of myeloid cells in glioblastoma across species and disease stage reveals macrophage competition and specialization. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24:595‐610. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

