Targeting olfactory receptor OR2AT4: An innovative aptamer-based treatment for hair growth promotion
- PMID: 40686857
- PMCID: PMC12272763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102608
Targeting olfactory receptor OR2AT4: An innovative aptamer-based treatment for hair growth promotion
Abstract
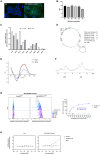
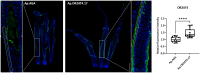
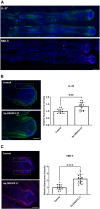
Non-canonical functions of olfactory receptors, one of the largest families of GPCR receptors not confined to the olfactory system, include an intriguing role on hair physiology. Previous studies using odorant agonists of the Olfactory Receptor family 2 subfamily AT member 4 (OR2AT4) showed hair growth stimulation. To develop more effective topical or systemic treatments for hair growth by specifically activating this receptor, it is crucial to identify new molecules with potent and well-defined activity. Here, we present a significant advancement in targeted therapeutic strategies for hair loss through the identification of a highly specific DNA aptamer targeting OR2AT4. The selected aptamer, designed as Ap.OR2AT4.17, effectively prolonged the anagen phase of hair growth cycle in a valuable preclinical human organ culture model. Importantly, the identified OR2AT4 aptamer was shown to be functional, leading to enhanced OR2AT4 expression in hair follicles, increased proliferation of hair matrix keratinocytes, and significant hair shaft elongation in organ-cultured human hair follicles. Notably, aptamer treatment also upregulated LL-37 and human β defensin-3 antimicrobial peptide expression, highlighting its role as a microbiota-modulating compound. These findings underscore the OR2AT4 aptamer's potential as a novel, targeted therapy for hair loss disorders, marking a promising step forward in the field.
Keywords: LL-37; MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; OR2AT4; alopecia; antimicrobial peptides; aptamer; olfactory receptor; β defensin-3.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.M., N.I., M.d.C.d.A., E.M., F.L., V.M.G., M.D.R., F.J., and M.C. declare that a patent application has been filed relating to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Wu C., Xu M., Dong J., Cui W., Yuan S. The structure and function of olfactory receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024;45:268–280. - PubMed
-
- Denda M., Nakanishi S. Do epidermal keratinocytes have sensory and information processing systems? Exp. Dermatol. 2022;31:459–474. - PubMed
-
- Busse D., Kudella P., Grüning N.M., Gisselmann G., Ständer S., Luger T., Jacobsen F., Steinsträßer L., Paus R., Gkogkolou P., et al. A synthetic sandalwood odorant induces wound-healing processes in human keratinocytes via the olfactory receptor OR2AT4. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2014;134:2823–2832. - PubMed
-
- Tsai T., Veitinger S., Peek I., Busse D., Eckardt J., Vladimirova D., Jovancevic N., Wojcik S., Gisselmann G., Altmüller J., et al. Two olfactory receptors-OR2A4/7 and OR51B5-differentially affect epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2017;26:58–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

