Effects of DBD-CP pre-treatment on muscle quality, volatile flavor compounds, and microbial community composition of ready-to-eat drunken shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) during frozen storage
- PMID: 40686906
- PMCID: PMC12270935
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102723
Effects of DBD-CP pre-treatment on muscle quality, volatile flavor compounds, and microbial community composition of ready-to-eat drunken shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) during frozen storage
Abstract
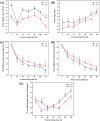
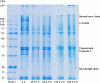
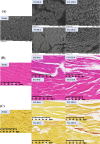
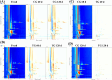
This study primarily investigated the effects of cold plasma generated by dielectric barrier discharge (DBD-CP) pre-treatment on the physicochemical properties, microbial community composition, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) of ready-to-eat drunken shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) during frozen storage. The results indicated that the DBD-CP pre-treatment reduced the relative abundance of microorganisms, significantly inhibited microbial growth and slowed the oxidation and degradation of muscle proteins. Furthermore, DBD-CP pre-treatment effectively maintained a stable structure of muscle fibers during frozen storage at -18 °C. Gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) analysis identified 26 volatile components, including 8 alcohols, 6 esters, 6 ketones, 3 aldehydes, and 3 other compounds in the drunken shrimp after DBD-CP pre-treatment. DBD-CP pre-treatment significantly influenced the VOCs during the frozen storage. This study provides a reference for further research on the quality of drunken shrimp.
Keywords: DBD-CP pre-treatment; Hydrochloric acid (PubChem CID 313); Magnesia (PubChem CID 14792); Microorganism; Myofibrillar proteins; Potassium chloride (PubChem CID 4873); Ready-to-eat drunken shrimp; Trichloroacetic acid (PubChem CID 6421); Volatile organic compounds; Water (PubChem CID 962).
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Bahuaud D., Mørkøre T., Langsrud Ø., Sinnes K., Veiseth E., Ofstad R., et al. Effects of 1.5°C super-chilling on quality of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) pre-rigor fillets: Cathepsin activity, muscle histology, texture and liquid leakage[J] Food Chemistry. 2008;111(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.03.075. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Caglayan C., Taslimi P., Türk C., Kandemir M.F., Demir Y., Gulcin İ. Purification and characterization of the carbonic anhydrase enzyme from horse mackerel (Trachurus trachurus) muscle and the impact of some metal ions and pesticides on enzyme activity[J] Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C. 2019;226, Article 108605 doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2019.108605. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaillou S., Chaulot-Talmon A., Caekebeke H., Cardinal M., Christieans S., Denis C., et al. Origin and ecological selection of core and food-specific bacterial communities associated with meat and seafood spoilage[J] The ISME Journal. 2015;9(5):1105–1118. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2014.202. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng J.H., Li J., Sun D.W. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on structure, surface hydrophobicity and allergenic properties of shrimp tropomyosin[J] Food chemistry. 2023;409 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

