Effect of thermomechanical aging on fracture strength of anterior crowns fabricated with different CAD-CAM materials
- PMID: 40687195
- PMCID: PMC12270717
- DOI: 10.4047/jap.2025.17.3.158
Effect of thermomechanical aging on fracture strength of anterior crowns fabricated with different CAD-CAM materials
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of thermomechanical aging on fracture strength of CAD/CAM (computer aided design and computer aided manufacturing) anterior crowns.
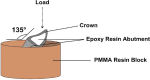
Materials and methods: A resin maxillary central incisor was prepared and 96 epoxy resin replicas were obtained. Anterior crowns were produced and divided into four groups: IPS (IPS e.max CAD, 1.5 mmthickness), CD (Celtra Duo, 1.5 mm thickness), GC (GC Initial UHT, 1.5 mm thickness) and GC1 (GC Initial UHT, 1 mm thickness). Twelve crowns of each group were subjected to a chewing simulator for 240,000 cycles, and the other 12 crowns were regarded as control. Fracture resistance of aged and non-aged crowns were tested using a universal testing machine (Shimadzu AGS-X). One-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc and independent sample t-tests were used to analyze the data and a P value < .05 was considered significant.
Results: IPS crowns without aging had the highest (2094.3 ± 399.31 N), and the GC1 crowns after aging had the lowest (1216.99 ± 302.96 N) fracture strength values. The difference of fracture strength among the same thickness samples without aging was not statistically significant (P > .05). The fracture strength of the GC1 group was significantly lower than those of the other groups (P < .05). After aging; GC group showed significantly higher fracture strength than the IPS and GC1 groups. The CD group's fracture strength was significantly higher than the GC1 group (P < .05). Aging significantly decreased the fracture strength of the IPS group (P < .05).
Conclusion: All monolithic crowns employed in this research proved to be resistant to physiological chewing forces in the anterior region.
Keywords: Anterior crown; CAD-CAM; Chewing simulator; Fracture strength; Zirconia reinforced lithium silicate.
© 2025 The Korean Academy of Prosthodontics.
Figures


References
-
- Conrad HJ, Seong WJ, Pesun IJ. Current ceramic materials and systems with clinical recommendations: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2007;98:389–404. - PubMed
-
- Altamimi AM, Tripodakis AP, Eliades G, Hirayama H. Comparison of fracture resistance and fracture characterization of bilayered zirconia/fluorapatite and monolithic lithium disilicate all ceramic crowns. Int J Esthet Dent. 2014;9:98–110. - PubMed
-
- Gehrt M, Wolfart S, Rafai N, Reich S, Edelhoff D. Clinical results of lithium-disilicate crowns after up to 9 years of service. Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17:275–284. - PubMed
-
- Pieger S, Salman A, Bidra AS. Clinical outcomes of lithium disilicate single crowns and partial fixed dental prostheses: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2014;112:22–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

