FBXO32 promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating NME1
- PMID: 40687258
- PMCID: PMC12268887
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2426
FBXO32 promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating NME1
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer, a common cancer, has a high incidence rate, the 5-year survival rate of gastric cancer with distant metastasis is less than 10%, so finding new targets for gastric cancer is of clinical importance. As a member of the F-box protein family, F-box protein 32 (FBXO32) plays a role in various cancers, but its role in gastric cancer is currently unclear, this study mainly focused on the role and mechanism of FBXO32 in gastric cancer.
Methods: The FBXO32 expression was found through The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The FBXO32 expression in cell lines was found through Western blot assay. Cell cloning assay and Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) assay were used to investigate the effect of FBXO32 on gastric cancer cell proliferation. Wound-healing assay and transwell assay were used to research the effect of FBXO32 on gastric cancer cell metastasis. Cancer stem cell sphere-forming assay was used to find out the effect of FBXO32 on the stemness of gastric cancer cells. Nude mouse tumorigenesis assay was used to investigate the effect of FBXO32 on gastric cancer tumor growth.
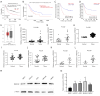
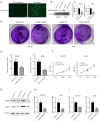
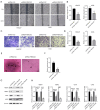
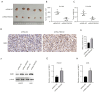
Results: It was found that FBXO32 expression is elevated in gastric cancer, which is associated with poor prognosis. In addition, FBXO32 expression is also elevated in gastric cancer cell lines. The knockdown of FBXO32 can inhibit the proliferation, migration, invasion and stemness of gastric cancer cells, inhibit the subcutaneous tumor formation of gastric cancer cells in nude mice, and increase the expression of non-metastatic cells 1 (NME1). Low expression of NME1 is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. The knockdown of NME1 expression can offset part of the tumor suppressor activity of the knockdown of FBXO32.
Conclusions: It is believed that FBXO32 promotes the progression of gastric cancer by regulating NME1. Most importantly, our findings could provide information for the mechanism of gastric cancer and the discovery of new targets.
Keywords: F-box protein 32 (FBXO32); gastric cancer; non-metastatic cells 1 (NME1).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-2024-2426/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
M1 Macrophage-Derived TNF-α Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Ferroptosis Via p38 MAPK-ACSL4 Pathway.Curr Mol Med. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.2174/0115665240374551250630075409. Online ahead of print. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40653839
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin αVβ1-activated PYK2 promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the STAT3-VGF axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jun 6;22(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01639-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38844957 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
[Expression of SIPA1 in colorectal cancer and its impact on its biological behavior].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 23;47(7):657-668. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20240812-00338. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40692252 Chinese.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
