A review of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer: insights into biomarker discovery and therapeutic targeting
- PMID: 40687415
- PMCID: PMC12270854
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1549046
A review of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer: insights into biomarker discovery and therapeutic targeting
Abstract
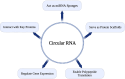
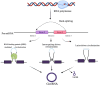
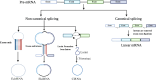
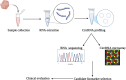
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers, with an incidence that has increased significantly over the last 20 years. The World Health Organization (WHO), under its cancer program, identifies CRC as the third most prevalent cancer worldwide with a high mortality rate, especially in patients under the age of 50. Despite advances in surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and molecular targeted therapy, CRC shares a low survival rate and poor prognosis due to late diagnosis. To address these challenges, research into alternative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies has increasingly focused on molecular mechanisms, including noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a subclass of endogenous ncRNAs characterized by their covalently enclosed loop structure, demonstrate greater stability than linear RNAs, making them potential candidates for clinical applications. The circRNAs possess differential expressions in cancers and function as tumor suppressive or oncogenic activities. This review discusses the recent findings on circRNAs and their potential for biomarkers and therapeutic targets in CRC. As circRNAs can serve as miRNA sponges, increase or decrease mRNA expression, and function to regulate an oncogenic or tumor suppressor pathway, there may be the possibility for an early diagnosis, prognosis, or therapeutic role of circRNAs in CRC. Highlighting the clinical implications of circRNAs, this review discusses their potential to transform current CRC management strategies and address critical gaps in timely diagnosis and effective treatment. It also emphasized the need for further clinical research to validate their utility and translate these findings into practice.
Keywords: biomarker; circular RNA; colorectal cancer; diagnosis; miRNA sponges; noncoding RNA; prognosis.
Copyright © 2025 Nambidi, Shruthi, Kanimozhe, Banerjee, Kondaveeti, Duttaroy and Pathak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Al-Joufi F, Setia A, Salem-Bekhit M, Sahu R, Alqahtani F, Widyowati R, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer with an emphasis on recent advances in biomarkers, as well as nanotechnology-based diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Nanomaterials. (2022) 12:169. doi: 10.3390/nano12010169 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

