BCAA metabolism: the Achilles' heel of ovarian cancer, polycystic ovary syndrome, and premature ovarian failure
- PMID: 40687583
- PMCID: PMC12270879
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1579477
BCAA metabolism: the Achilles' heel of ovarian cancer, polycystic ovary syndrome, and premature ovarian failure
Abstract
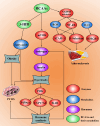
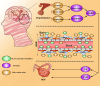
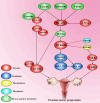
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), including valine, leucine and isoleucine, are essential nutrient signals that influence mammalian animal metabolism. Many enzymes are involved in the metabolism of BCAAs, such as branched-chain amino acid transaminases (BCATs), branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKDH), and BCKDH kinase (BCKDK). The aberrant expression of enzymes involved in BCAA metabolism and an imbalance in BCAA amino acid intake can lead to disordered metabolism. Aberrant BCAA metabolism can lead to several diseases, such as human ovarian disease, including ovarian cancer (OC), polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and premature ovarian failure (POF), which are common gynaecological diseases. The overexpression of BCATs is found in OC, which promotes BCAA catalysis to provide a large amount of energy for tumorigenesis. However, BCKDK is overexpressed in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), which promotes proliferation and migration via MEK-ERK. In addition, several studies have reported that high levels of BCAAs are increased in the plasma of PCOS and POF patients. This review focuses on the role of BCAA metabolism and potential management methods for OC, PCOS and POF.
Keywords: branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs); human ovarian disease; metabolism; polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS); premature ovarian failure (POF).
Copyright © 2025 Zeng, Liu, Tang, Fu, Gao, Zhou, Fang, Zhang, Zou and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

