Logistic regression analysis of pregnancy outcome and EFI score of infertile patients with ovarian endometriosis cyst after staged oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 40687588
- PMCID: PMC12270884
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1624925
Logistic regression analysis of pregnancy outcome and EFI score of infertile patients with ovarian endometriosis cyst after staged oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
Background: Ovarian endometriosis cysts are associated with infertility, and recent research increasingly focuses on improving pregnancy outcomes. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has long been used for gynecological issues, yet the impact of staged TCM administration on pregnancy outcomes and Endometriosis Fertility Index (EFI) scores in infertile patients remains underexplored.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the effects of staged TCM administration on pregnancy outcomes and EFI scores in patients with ovarian endometriosis cysts.
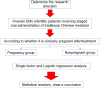
Method: A retrospective analysis of 150 infertile patients treated with staged TCM administration was conducted. Patients received Formula I before ovulation and Formula II post-ovulation, with the cohort split into pregnancy (n=91) and non-pregnancy groups (n=49). All patients underwent laparoscopic surgery prior to TCM treatment. Logistic regression and ROC analysis were used to assess pregnancy predictors.
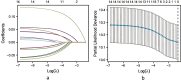
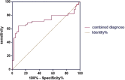
Results: Significant differences in age, infertility type, infertility duration, r-AFS stage, cyst diameter, and EFI score (P<0.05) were found. Age, secondary infertility, infertility duration (≥3 years), advanced r-AFS stage, cyst diameter (≥3cm), and EFI score (<7) were key risk factors. The EFI score's AUC for predicting pregnancy was 0.731 (95%CI, 0.617-0.844), with 72.58% sensitivity and 75.83% specificity. No significant difference in follow-up duration was observed between the groups.
Conclusion: Age, secondary infertility, infertility duration (≥ 3 years), r-AFS stage (stages III and IV), cyst diameter (≥ 3cm), and EFI score (< 7) were identified as risk factors for infertility in patients with ovarian endometriosis following a two-phase staged oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine. Among these factors, the EFI score can serve as a crucial evaluation index for postoperative pregnancy, assessing the likelihood of pregnancy and predicting patient prognosis.
Keywords: EFI score; infertility risk factors; ovarian endometriosis cyst; pregnancy outcome; staged oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Bo, Peng, Su and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ovarian endometriosis negatively impacts pregnancy outcomes in young infertile women undergoing IVF/ICSI treatment.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 2;30(1):555. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02816-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40604864 Free PMC article.
-
Pentoxifylline for the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain and infertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 25;8(8):CD007677. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007677.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34431079 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD006568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006568.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22592712
-
Chinese herbal medicine for endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jul 8;(3):CD006568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD006568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006568.pub3. PMID: 19588398 Updated.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 5;(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. PMID: 23913583 Updated.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

