Leveraging multiple labeled datasets for the automated annotation of single-cell RNA and ATAC data
- PMID: 40687986
- PMCID: PMC12270792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.06.043
Leveraging multiple labeled datasets for the automated annotation of single-cell RNA and ATAC data
Abstract
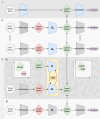
The creation of single-cell atlases is essential for understanding cellular diversity and heterogeneity. However, assembling these atlases is challenging due to batch effects and the need for accurate and consistent cell annotation. Current methods for single-cell RNA and ATAC sequencing (scRNA-Seq and scATAC-Seq), while effective for integration, are not optimized for cell annotation. Additionally, many annotation tools rely on external databases or reference scRNA-Seq datasets, which may limit their adaptability to specific study needs, especially for rare cell-types or scATAC-Seq data. Here, we introduce JIND-Multi, a new framework designed to transfer cell-type labels across multiple annotated datasets. Notably, JIND-Multi can be applied to both scRNA-Seq and scATAC-Seq data, requiring in each case annotated data of the same type, contrary to most methods for scATAC-Seq data that require (paired) annotated scRNA-Seq data. In both cases, JIND-Multi significantly reduces the proportion of unclassified cells while maintaining the accuracy and performance of the original JIND model, and compares favorable to state-of-the-art methods. These results prove its versatility and effectiveness across different single-cell sequencing technologies. JIND-Multi represents an improvement in cell annotation, reducing unassigned cells and offering a reliable solution for both scRNA-Seq and scATAC-Seq data. Its ability to handle multiple labeled datasets enhances the precision of annotations, making it a valuable tool for the single-cell research community. JIND-Multi is publicly available at: https://github.com/ML4BM-Lab/JIND-Multi.git.
Keywords: Cell-type annotation; Data integration; Deep learning; Neural networks; Single-cell atlases; scATAC-Seq; scRNA-Seq.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
