Relationship between serum copeptin levels and non-invasive endothelial function indicators in dipper and non-dipper hypertensive patients
- PMID: 40689062
- PMCID: PMC12267084
- DOI: 10.62347/TSLN4765
Relationship between serum copeptin levels and non-invasive endothelial function indicators in dipper and non-dipper hypertensive patients
Abstract
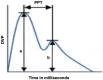
Objective: Pathological changes in the endothelium are the earliest determinants of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in hypertension (HT). The diagnostic and prognostic role of copeptin in various diseases is well-recognized. This study aims to investigate the relationship between serum copeptin levels and non-invasive endothelial function indicators determined by flow-mediated dilation (FMD) and pulse wave analysis (PWA) in dipper and non-dipper HT patients.
Methods: In this study, 30 dipper HT, 31 non-dipper HT patients and 30 healthy control subjects were included. Blood samples were taken for copeptin level determination. All participants underwent detailed cardiovascular and transthoracic echocardiography examinations and measurements of FMD and PWA.
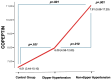
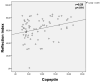
Results: Copeptin levels of the non-dipper HT group were significantly higher than the control group and dipper HT groups (P=.001, P=.010, respectively). No significant difference was found between the dipper and non-dipper HT groups regarding FMD and PWA measurements, and both groups significantly differed from the control group. In the whole group evaluation by partial correlation analysis, a significant correlation was found between serum copeptin levels and reflection index (RI) after adjustment for age and body mass index (r=0.24, P=.039). Stepwise linear regression analysis revealed RI as an independent predictor of copeptin (β=0.285, P=.015).
Conclusion: The correlation between copeptin levels and RI in HT patients, especially in the non-dipper HT group, suggests that copeptin can be used as a biomarker to indicate endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive patients.
Keywords: Arginine vasopressin; arterial stiffness; copeptin; endothelium; flow-mediated dilation; hypertension; pulse wave analysis.
AJCD Copyright © 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global report on hypertension: the race against a silent killer. World Health Organization. 2023
-
- Falaschetti E, Chaudhury M, Mindell J, Poulter N. Continued improvement in hypertension management in England: results from the Health Survey for England 2006. Hypertension. 2009;53:480–486. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
