Key factors influencing orthopaedic operating room contamination: Impact of human activity and Staphylococcus epidermidis prevalence
- PMID: 40689095
- PMCID: PMC12272502
- DOI: 10.1002/jeo2.70321
Key factors influencing orthopaedic operating room contamination: Impact of human activity and Staphylococcus epidermidis prevalence
Abstract
Purpose: The presence of pathogen microorganisms in the operating room remains a significant concern. This study aims to explore the factors influencing the presence of pathogens in the operating room.
Methods: We analysed the presence of microorganisms in the operation theatre during total knee and hip replacement procedures for 33 patients performed in the same operation room (OR) over a period of 2 months. Three hundred and ninety-six samples were taken from several areas belonging to the sterile field. We have also analysed behavioural aspects in the OR that could influenced the potential contamination of the sterile field, such as the number of touches of the lamps, the temperature in the OR, the height of the operating table, the number of door openings.
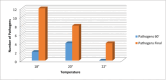
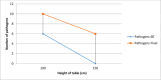
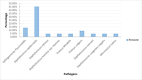
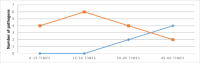
Results: Out of the total of 396 samples, 74 were positive. Most contaminations were with Staphylococcus epidermidis (45.45%). Most pathogens were found on the instrument table at the end of the intervention (27.27%). There is a correlation regarding the fact that at lower heights, the risk of contamination higher than if the table is raised more. We also find correlations between the number of operating room doors opened and the presence of field contamination, as well as between the number of touches of the lamps and the presence of pathogens on sterile fields.
Conclusion: The presence of pathogens in the OR is influenced by the number of lamp touches, the frequency of door openings, and the increased number of people in the room. However, temperature and the height of the operating table do not have a significant impact on the occurrence of pathogens. The most commonly found pathogen in the OR was S. epidermidis. At the end of the surgery, the instrument table showed the highest percentage of pathogen presence.
Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
Keywords: Staphylococcus; hip; knee; operating room; orthopaedic.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is Your Surgical Helmet System Compromising the Sterile Field? A Systematic Review of Contamination Risks and Preventive Measures in Total Joint Arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 1;483(6):972-990. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003383. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39915114
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Active body surface warming systems for preventing complications caused by inadvertent perioperative hypothermia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 21;4(4):CD009016. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009016.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27098439 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Pharmacological interventions for the prevention of bleeding in people undergoing elective hip or knee surgery: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jan 16;1(1):CD013295. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013295.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38226724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Laham N. Distribution and antimicrobial resistance pattern of bacteria isolated from operation theaters at Gaza Strip. J Al Azhar Univ Gaza. 2012;14:19–34.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

