Deep Neuromuscular Block with Low Pressure Pneumoperitoneum in Laparoscopic Abdominal Surgeries: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40689105
- PMCID: PMC12275633
- DOI: 10.5812/aapm-150995
Deep Neuromuscular Block with Low Pressure Pneumoperitoneum in Laparoscopic Abdominal Surgeries: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Postoperative pain management remains a challenge in laparoscopic abdominal surgeries.
Objectives: The purpose of this research was to determine the effects of deep neuromuscular blockade (NMB) in conjunction with low-pressure pneumoperitoneum )PP) on postoperative pain, surgical parameters, and recovery outcomes.
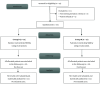
Methods: This randomized controlled double-blind study included 44 participants undergoing laparoscopic abdominal surgery. Patients were randomized equally into two groups (22 each): Group D received deep NMB, while group M received moderate NMB using cis-atracurium, through the utilization of computer-generated random numbers enclosed within sealed, opaque envelopes, following a parallel approach. Regarding deep NMB, following an initial dose of 0.15 mg/kg, a continuous infusion of 0.06 - 0.12 mg/kg/hr was administered to maintain a post-tetanic count between 1 and 2, with low PP pressure of 10 - 12 mmHg. Conversely, for moderate NMB, after the same initial dose of 0.15 mg/kg, the continuous infusion commenced upon the train-of-four count returning to 2, with the rate adjusted to sustain a count between 1 and 3, and standard PP pressure of 15 mmHg. The primary outcome was postoperative pain intensity as measured by Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) scores in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU). The secondary outcomes included postoperative pain intensity measured by NRS scores from 2 hours to 48 hours post-surgery, time to first analgesic administration, cumulative opioid consumption within the initial 48-hour postoperative period, and patient-reported satisfaction with postoperative pain management. Statistical analysis using SPSS v26 included tests for normality (Shapiro-Wilks), with parametric data analyzed by t-test, non-parametric data by Mann-Whitney, and qualitative data by chi-square/Fisher's test.
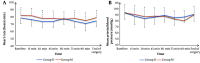
Results: Group D experienced a considerably longer time until the first analgesic rescue compared to group M (9.82 ± 1.5 hours vs. 7.23 ± 1.19 hours, P < 0.001). Morphine consumption in the first 24 hours was lower in Group D (10.77 ± 1.51 mg vs. 13.09 ± 1.74 mg, P < 0.001). At 6, 8, and 12 hours postoperatively, group D exhibited significantly lower pain scores (P < 0.05). Surgical duration, surgical field quality, complication rates, and patient satisfaction were comparable between groups.
Conclusions: Deep NMB combined with low-pressure PP provided superior postoperative analgesia without compromising surgical field quality or increasing complications in laparoscopic abdominal surgeries.
Keywords: Laparoscopic; Low Pressure; Neuromuscular Block; Pneumoperitoneum; Postoperative Pain.
Copyright © 2024, Mohamed Ibrahim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of sugammadex versus neostigmine in reversing neuromuscular blockade in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 14;8(8):CD012763. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012763. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28806470 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous intravenous perioperative lidocaine infusion for postoperative pain and recovery in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 4;6(6):CD009642. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009642.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29864216 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone as an adjuvant to peripheral nerve block.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 9;11(11):CD011770. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011770.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29121400 Free PMC article.
-
Ketorolac for postoperative pain in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 7;7(7):CD012294. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012294.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29981164 Free PMC article.
-
Single-dose intravenous diclofenac for acute postoperative pain in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 28;8(8):CD012498. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012498.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30153336 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous