Ferroptosis as a potential therapeutic target for obesity-related metabolic diseases
- PMID: 40689204
- PMCID: PMC12272611
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1581632
Ferroptosis as a potential therapeutic target for obesity-related metabolic diseases
Abstract
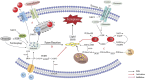
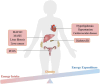
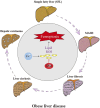
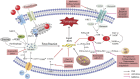
Obesity represents one of the major public health issues threatening the global health and promoting chronic metabolic disorders, including type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance (IR), hyperlipidemia, hypertension, polycystic ovary syndrome, metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), and others. Ferroptosis, a novel form of cell death, is a programmed cell death induced by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation. It is characterized by excessive iron accumulation and unregulated lipid peroxidation. The activity of ferroptosis is modulated by multiple factors such as iron, reactive oxygen species, and over 98 unsaturated fatty acids. Mounting evidence indicates that ferroptosis plays a crucial role in obesity-related chronic metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes, IR, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, polycystic ovary syndrome, and MAFLD. Clarifying the molecular mechanism of ferroptosis may discover potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of these diseases. This article comprehensively reviews the role, pathogenesis, prevention, treatment strategies, current research gaps and future development directions of ferroptosis in obesity-related chronic metabolic diseases have been thoroughly discussed, and novel perspectives for the future treatment and research of ferroptosis in these diseases carefully provided. It points out directions for basic research on ferroptosis, raises urgent needs for developing precise intervention strategies, and provides new insights into the treatment and study of obesity-related chronic metabolic diseases in the future.
Keywords: ferroptosis; obesity-related metabolic diseases; occurrence and regulation of ferroptosis; pharmacotherapy strategy; potential therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Luo, Zhang, Cheng, Peng, Zhou, Cao, Chen, He, Chen, Zhang, Zhang and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Author CC declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Adamska A., Łebkowska A., Krentowska A., Hryniewicka J., Adamski M., Leśniewska M., et al. (2020). Ovarian reserve and serum concentration of thyroid peroxidase antibodies in euthyroid women with different polycystic ovary syndrome phenotypes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11 (undefined), 440. 10.3389/fendo.2020.00440 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

