The Role of p66Shc in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 40690563
- PMCID: PMC12279043
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70737
The Role of p66Shc in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
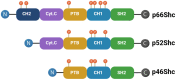
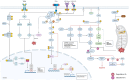
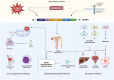
p66Shc is a redox-sensitive and pro-apoptotic adaptor protein that regulates oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis. It is the largest of three isoforms encoded by the proto-oncogene ShcA (Src collagen homologue A). Members of the ShcA family are capable of recruiting various signalling molecules and are involved in several cellular pathways, including proliferation, growth and survival. Increasing evidence highlights the p66Shc role in various tumourigenic processes, such as cell expansion, progression, metastasis and metabolic reprogramming. This review summarises current knowledge on the role of p66Shc in cancer, explains the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of this protein, and considers therapeutic prospects aimed at targeting it. Emerging therapeutic strategies, including small-molecule inhibitors and gene-editing approaches, are discussed alongside challenges in clinical translation.
Keywords: cancer; p66Shc; reactive oxygen species; signalling pathway.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

