Mechanism of Rad51 filament formation by Rad52 and Rad55-Rad57 in homologous recombination
- PMID: 40691144
- PMCID: PMC12280074
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61811-0
Mechanism of Rad51 filament formation by Rad52 and Rad55-Rad57 in homologous recombination
Abstract
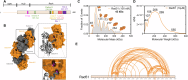
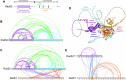
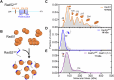
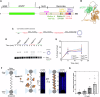
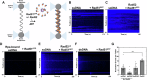
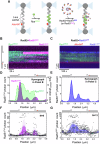
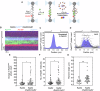
Homologous recombination (HR) repairs double-stranded DNA breaks (DSBs) by generating single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), which is initially coated by Replication Protein A (Rpa). Rad51, a recombinase, catalyzes strand invasion but binds ssDNA with lower affinity than Rpa, necessitating mediator proteins like Rad52 (yeast) or BRCA2 (humans) for Rad51 loading. The mechanisms of this exchange remain unclear. We show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad52 uses its disordered C-terminus to sort polydisperse Rad51 into discrete monomers. Using fluorescent-Rad51 and single-molecule optical tweezers, we visualize Rad52-mediated Rad51 filament formation on Rpa-coated ssDNA, preferentially at ssDNA-dsDNA junctions. Deleting the C-terminus of Rad52 disrupts Rad51 sorting and loading. Addition of the Rad51 paralog Rad55-Rad57 enhances Rad51 binding by ~60%. Despite structural differences, Rad52 and BRCA2 share conserved functional features. We propose a unified "Sort, Stack & Extend" (SSE) mechanism by which mediator proteins and paralogs coordinate Rad51 filament assembly during HR.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Negrini, S., Gorgoulis, V. G. & Halazonetis, T. D. Genomic instability-an evolving hallmark of cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.11, 220–228 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Pfeiffer, P., Goedecke, W. & Obe, G. Mechanisms of DNA double-strand break repair and their potential to induce chromosomal aberrations. Mutagenesis15, 289–302 (2000). - PubMed
-
- San Filippo, J., Sung, P. & Klein, H. Mechanism of eukaryotic homologous recombination. Annu. Rev. Biochem.77, 229–257 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM137751/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10OD030343/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- S10 OD028650/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM149320/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10OD28650/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- R01GM137751/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R01GM58015/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35GM149320/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35GM122569/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- P20GM103474/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35 GM122569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM058015/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030343/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103474/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

