Ribosomal protein mutation suppresses gonadal leader cell migration defects in mig-17/ADAMTS mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 40691188
- PMCID: PMC12280101
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-10316-3
Ribosomal protein mutation suppresses gonadal leader cell migration defects in mig-17/ADAMTS mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
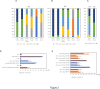
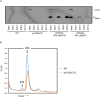
The migration of gonadal distal tip cells (DTCs) in Caenorhabditis elegans serves as an excellent model for studying the migration of epithelial tubes during organogenesis. Mutations in the mig-17/ADAMTS gene cause misdirected DTC migration during gonad formation, resulting in deformed gonad arms. An amino acid substitution in RPL-20, the ortholog of mammalian RPL18a/eL20, a component of the 60 S ribosomal large subunit, exhibited a slow-growth phenotype and strongly suppressed the mig-17 gonadal defects. Slow-growing mutations clk-1 and clk-2 also suppressed mig-17. Intestine-specific overexpression of mutant RPL-20 protein resulted in a slow-growth phenotype and suppressed the mig-17 gonadal defects, but these effects were much weaker when wild-type RPL-20 was overexpressed, suggesting that the mutant RPL-20 protein acquired a novel function. Analysis of ribosome profiles revealed reduced biogenesis of the 60 S subunit, leading to a reduction of 80 S ribosomes in the rpl-20 mutant. These results suggest that DTC migration defects in mig-17/ADAMTS mutants can be partly suppressed by growth retardation caused by the rpl-20 mutation. While defective ribosome biogenesis may contribute to the observed growth retardation, further investigation is needed to clarify the molecular basis of this phenomenon.
Keywords: ADAMTS; Growth retardation; Organogenesis; RPL18a/eL20; Ribosome protein mutation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic interactions among ADAMTS metalloproteases and basement membrane molecules in cell migration in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 2;15(12):e0240571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240571. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33264296 Free PMC article.
-
The novel secreted factor MIG-18 acts with MIG-17/ADAMTS to control cell migration in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2014 Feb;196(2):471-9. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.157685. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24318535 Free PMC article.
-
The Rac pathway prevents cell fragmentation in a nonprotrusively migrating leader cell during C. elegans gonad organogenesis.Curr Biol. 2024 Jun 3;34(11):2387-2402.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.04.073. Epub 2024 May 21. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 38776905 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Russell, D. L., Doyle, K. M., Ochsner, S. A., Sandy, J. D. & Richards, J. S. Processing and localization of ADAMTS-1 and proteolytic cleavage of versican during cumulus matrix expansion and ovulation. J. Biol. Chem.278, 42330–42339. 10.1074/jbc.M300519200 (2003). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

