A 5-year prospective assessment of risk factors for lower limb lymphedema after gynecologic cancer surgery
- PMID: 40691210
- PMCID: PMC12280194
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11732-1
A 5-year prospective assessment of risk factors for lower limb lymphedema after gynecologic cancer surgery
Abstract
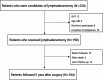
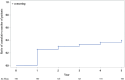
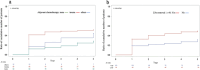
Lower limb lymphedema is a distressing complication after lymphadenectomy. Currently, no definite intervention for reducing the incidence of lower limb lymphedema has been established. This study identified risk factors for lower limb lymphedema following a gynecologic surgery with a 5-year follow-up. A total of 190 patients who underwent surgery, including pelvic lymphadenectomy, between 2011 and 2012 were enrolled and followed up for 5 years. Lymphedema was defined as International Society of Lymphology stage I or higher. The patients' physical characteristics, surgical methods, and adjuvant therapies were investigated and hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to assess the 5-year cumulative risk of lower limb lymphedema. Multivariate analysis revealed that adjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel or paclitaxel and the number of lymph nodes removed ≥ 60 were the risk factors. The 5-year cumulative incidence of total lower limb lymphedema was 39.6%, 51.6% with adjuvant chemotherapy using taxanes, 49.1% with the removal of ≥ 60 lymph nodes. The incidence of lower limb lymphedema was highest in the first year. Since taxane administration and lymphadenectomy remain essential for optimizing patient prognosis, close monitoring of lower limbs is crucial in the first year after lymphadenectomy for patients with these risk factors.
Keywords: Adjuvant chemotherapy; Docetaxel; Gynecologic cancer; Lower limb lymphedema; Lymphadenectomy; Risk factors.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This study was approved by the IRB of Cancer Institute Hospital of the Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research (No. 2011 − 1027). Informed consent: Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence, classification, and risk factors for postoperative lower extremity lymphedema in women with gynecologic malignancies: a retrospective study.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015 May;25(4):751-7. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000405. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25723779
-
Lymphadenectomy for the management of endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 2;10(10):CD007585. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007585.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28968482 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphadenectomy for the management of endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 21;2015(9):CD007585. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007585.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Oct 02;10:CD007585. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007585.pub4. PMID: 26387863 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Lymphadenectomy or sentinel node biopsy for the management of endometrial cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 10;6(6):CD015786. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015786.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40492478 Review.
-
Safety and Feasibility Analysis of Laparoscopic Lymphadenectomy in Pelvic Gynecologic Malignancies: A Prospective Study.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015 Nov;25(9):1704-10. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000000555. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26397158
References
-
- Todo, Y. et al. Risk factors for postoperative lower-extremity lymphedema in endometrial cancer survivors who had treatment including lymphadenectomy. Gynecol. Oncol.119, 60–64 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Kehoe, S. M. & Miller, D. S. The role of lymphadenectomy in endometrial cancer. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol.54, 235–244 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Panici, P. B. et al. Systematic pelvic lymphadenectomy vs, no lymphadenectomy in early-stage endometrial carcinoma: randomized clinical trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst.3, 1707–1716 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

