Wound healing properties and antibiofilm activity of hydrogel matrix containing nitric oxide, silver nanoparticles, and ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn wound infection
- PMID: 40691256
- PMCID: PMC12280077
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12385-w
Wound healing properties and antibiofilm activity of hydrogel matrix containing nitric oxide, silver nanoparticles, and ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa burn wound infection
Abstract
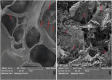
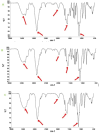
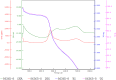
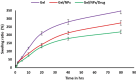
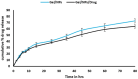
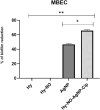
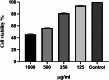
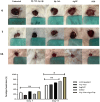
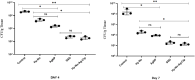
The high antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa has led to significant issues and delays in wound healing, resulting in disruptions to the healing process. The present study evaluated the antibacterial effects and wound healing properties of a hydrogel matrix containing nitric oxide, silver nanoparticles, and ciprofloxacin (Hy-NO-Ag-Cip) against multi-drug-resistant (MDR) P. aeruginosa. The MDR P. aeruginosa was isolated from patients with burn wound infection. Hy-NO-Ag-Cip was synthesized, and its physicochemical characteristics were evaluated. The in vitro antibacterial and anti-biofilm effects of Hy-NO-Ag-Cip were analyzed. Burn wound infections were induced in 25 rats, and topical application was conducted to assess the antibacterial efficacy and wound healing characteristics of Hy-NO-Ag-Cip. The results showed that the fabricated hydrogels have a porous structure, with interconnected pores. The spectra of the formulated hydrogel loaded with AgNPs and the drug showed bands with similar frequencies and shapes to those of the final hydrogel. The Hy-NO-Ag-Cip minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was 250 µg/mL, and the 2× MIC of this hydrogel reduced mature biofilm by 65%. There was no toxic effect observed at the MIC concentration of Hy-NO-Ag-Cip on the L929 cell line. In the wound healing process, the group treated with Hy-NO-Ag-Cip exhibited a greater epithelial thickness, indicating enhanced wound healing compared to the other group. Hy-NO-Ag-Cip enhances antibiotic accumulation at the infection site through a controlled drug release, resulting in a substantial antibacterial action and improved wound healing.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Antimicrobial resistance; Biofilms; Hydrogel matrix; Nitric oxide; Silver nanoparticles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Institutional Review Board (IR.UMSHA.REC.1402 133). Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antiseptics for burns.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 12;7(7):CD011821. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011821.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28700086 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the antibacterial and antibiofilm effect of mycosynthesized silver and selenium nanoparticles and their synergistic effect with antibiotics on nosocomial bacteria.Microb Cell Fact. 2025 Jan 4;24(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02604-w. Microb Cell Fact. 2025. PMID: 39755661 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting the healing of infected diabetic wound by nanozyme-containing hydrogel with anti-bacterial inflammation suppressing, ROS-scavenging and oxygen-generating properties.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024 Aug;112(8):e35458. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35458. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39122663
-
Antibiotic strategies for eradicating Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 25;4(4):CD004197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004197.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 2;6:CD004197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004197.pub6. PMID: 28440853 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sprayable ciprofloxacin loaded chitosan nanospheres-based topical formulation for eliminating multidrug-resistant bacteria and accelerating infected wound healing.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025 Oct;254:114880. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2025.114880. Epub 2025 Jun 15. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2025. PMID: 40532566
References
-
- Taherpour, A., Hashemi, A., Erfanimanesh, S. & Taki, E. Efficacy of methanolic extract of green and black teas against extended-spectrum beta-Lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pak J. Pharm. Sci.29 (4), 1257–1261 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

