Ultra-high-resolution imaging of intracranial flow diverters with photon counting CT: A comparative phantom study with flat-panel CT
- PMID: 40691292
- PMCID: PMC12280025
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12713-0
Ultra-high-resolution imaging of intracranial flow diverters with photon counting CT: A comparative phantom study with flat-panel CT
Abstract
Flow diverters are a crucial element in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. However, the optimal non-invasive follow-up imaging modality, particularly for the detection of in-stent stenosis, remains uncertain. This study aims to compare the performance of photon-counting detector CT (PCD-CT) in ultra-high-resolution (UHR) mode with flat-panel CT (FP-CT) for the evaluation of intracranial flow diverters. A phantom model for intracranial vessels was used to evaluate 15 flow diverters of various sizes and designs. Imaging was performed using both PCD-CT and FP-CT. Qualitative assessment of the stent lumen was conducted by three experienced neuroradiologists using a 5-point Likert scale. Quantitative analysis included measurements of lumen area, contrast to noise ratio and signal to noise ratio. FP-CT provided a significantly larger assessable stent lumen than PCD-CT at all dose levels (p < 0.05), with no significant differences between PCD-CT dose levels (p = 0.999). Increasing PCD-CT dose did not improve lumen visualization. SNR and CNR increased with PCD-CT dose (p < 0.001), peaking at CTDI 20, but showed diminishing returns beyond CTDI 10. Flow diverter diameter correlated positively with SNR and CNR (p < 0.05). Subjective image quality improved with PCD-CT dose (p < 0.001) but showed no significant difference beyond 10 mGy (p > 0.05). FRED devices had the lowest ratings, independent of imaging modality (p = 0.80). Our study demonstrated that while FP-CT provided superior visualization of the flow diverter lumen in a head phantom vessel model, subjective assessability ratings were comparable between FP-CT and PCD-CT when evaluated by experienced readers. PCD-CT at a CTDIvol of 10 mGy offered the best balance between image quality and radiation dose, making it a viable alternative for post-interventional assessment of flow diverters.
Keywords: Artifacts; Flat-panel CT; Flow diverter; Image quality; Ultra-high-resolution imaging.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
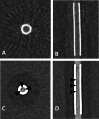
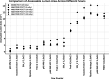

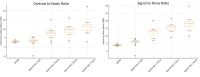
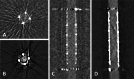
References
-
- Abel, F., Schubert, T. & Winklhofer, S. Advanced neuroimaging with Photon-Counting detector CT. Invest. Radiol.58, 472–481. 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000984 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Adolf, R. et al. Assessing beam hardening artifacts in coronary stent imaging using different CT acquisition parameters on photon-counting detector computed tomography. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging Doi. 10.1007/s10554-025-03392-z (2025). - PubMed
-
- Fiorella, D. et al. DEFINITIVE RECONSTRUCTION OF CIRCUMFERENTIAL, FUSIFORM INTRACRANIAL ANEURYSMS WITH THE PIPELINE EMBOLIZATION DEVICE. Neurosurgery62, 1115–1121. 10.1227/01.NEU.0000313128.12325.14 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

