Deep learning models to predict CO2 solubility in imidazolium-based ionic liquids
- PMID: 40691294
- PMCID: PMC12280190
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12004-8
Deep learning models to predict CO2 solubility in imidazolium-based ionic liquids
Abstract
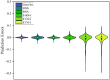
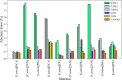
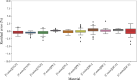
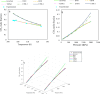
This study focuses on predicting CO2 solubility in imidazolium-based ionic liquids using deep learning models with input parameters of critical pressure, critical temperature, molecular weight, and acentric factor. The models evaluated include Bayesian Neural Networks (BNN), Deep Neural Networks (DNN), Gradient Boosting Neural Networks (GrowNet), Tabular Neural Networks (TabNet), Random Forest (RF), and Support Vector Regression (SVR). The results were compared with two PC-SAFT models, namely cQC-PC-SAFT-MSA (1) and cQC-PC-SAFT-MSA (2), where deep learning models performed better than SAFT models. Graphical and statistical analyses revealed that the GrowNet model, with a root mean square error of 0.0073 and a coefficient of determination of 0.9962, exhibited the lowest error compared to other models. In addition, Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) and Shapley additive description (SHAP) analyses highlighted pressure (P) as a key parameter determining CO2 solubility in imidazolium-based ionic liquids, significantly contributing to model performance.
Keywords: CO2 solubility; Deep learning; GrowNet; Imidazolium-based ionic liquids; TabNet.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
New insight into viscosity prediction of imidazolium-based ionic liquids and their mixtures with machine learning models.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22672. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08947-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595231 Free PMC article.
-
Machine and deep learning models for predicting high pressure density of heterocyclic thiophenic compounds based on critical properties.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 15;15(1):25465. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09600-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659686 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative assessment of standalone and hybrid deep neural networks for modeling daily pan evaporation in a semi-arid environment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 20;15(1):20179. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05985-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40542056 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence systems in dental shade-matching: A systematic review.J Prosthodont. 2024 Jul;33(6):519-532. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13805. Epub 2023 Dec 6. J Prosthodont. 2024. PMID: 37986239
-
Artificial intelligence for diagnosing exudative age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 17;10(10):CD015522. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015522.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39417312
References
-
- Lee, H. et al. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III To the Sixth Assessment Report.of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (The Australian National University, 2023).
-
- Al-qaness, M. A., Ewees, A. A., Elaziz, M. A. & Samak, A. H. Wind power forecasting using optimized dendritic neural model based on seagull optimization algorithm and aquila optimizer. Energies15, 9261 (2022).
-
- Safari, A., Das, N., Langhelle, O., Roy, J. & Assadi, M. Natural gas: A transition fuel for sustainable energy system transformation? Energy Sci. Eng.7, 1075–1094 (2019).
-
- Singh, U. & Colosi, L. M. The case for estimating carbon return on investment (CROI) for CCUS platforms. Appl. Energy285, 116394 (2021).
-
- Theo, W. L., Lim, J. S., Hashim, H., Mustaffa, A. A. & Ho, W. S. Review of pre-combustion capture and ionic liquid in carbon capture and storage. Appl. Energy183, 1633–1663 (2016).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

