NKX2-1 drives neuroendocrine transdifferentiation of prostate cancer via epigenetic and 3D chromatin remodeling
- PMID: 40691407
- PMCID: PMC12339387
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02265-4
NKX2-1 drives neuroendocrine transdifferentiation of prostate cancer via epigenetic and 3D chromatin remodeling
Abstract
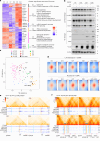
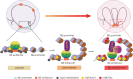
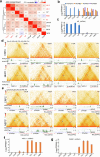
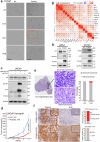
A substantial amount of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) progresses into a neuroendocrine (NE) subtype, known as NEPC, which is associated with poor clinical outcomes. Here we report distinct three-dimensional chromatin architectures between NEPC and CRPC tumors, which were recapitulated by isogenic cell lines undergoing NE transformation (NET). Mechanistically, pioneer factors such as FOXA2 initiate binding at NE enhancers to mediate regional DNA demethylation and induce neural transcription factor (TF) NKX2-1 expression. NKX2-1 preferentially binds gene promoters and interacts with enhancer-bound FOXA2 through chromatin looping. NKX2-1 is highly expressed in NEPC and indispensable for NET of prostate cancer. NKX2-1/FOXA2 further recruits p300/CBP to activate NE enhancers, and pharmacological inhibition of p300/CBP effectively blunts NE gene expression and abolishes NEPC tumor growth. Taken together, our study reports a hierarchical network of TFs governed by NKX2-1 in critically regulating chromatin remodeling and driving luminal-to-NE transformation and suggests promising therapeutic approaches to mitigate NEPC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













Update of
-
Epigenetic remodeling and 3D chromatin reorganization governed by NKX2-1 drive neuroendocrine prostate cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 7:2024.12.04.626816. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.04.626816. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Genet. 2025 Aug;57(8):1966-1980. doi: 10.1038/s41588-025-02265-4. PMID: 39677680 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA180995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA113913/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Center for Scientific Review (NIH Center for Scientific Review)
- PC220158/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- R01 CA286147/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- PC220151/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
- 2017CHAL2008/Prostate Cancer Foundation (PCF)
- R01CA257446/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R35 GM142539/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM142539/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Center for Scientific Review (NIH Center for Scientific Review)
- R50CA211271/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- P01 CA163227/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA180995/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R01 CA257446/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA286147/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R50 CA211271/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA097186/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA113913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- PC210266/U.S. Department of Defense (United States Department of Defense)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

