Estimation-uncertainty affects decisions with and without learning opportunities
- PMID: 40691426
- PMCID: PMC12280070
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61960-2
Estimation-uncertainty affects decisions with and without learning opportunities
Abstract
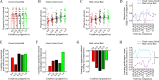
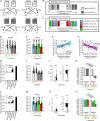
Motivated behavior during reinforcement learning is determined by outcome expectations and their estimation-uncertainty (how frequently an option has been sampled), with the latter modulating exploration rates. However, although differences in sampling-rates are inherent to most types of reinforcement learning paradigms that confront highly rewarded options with less rewarded ones, it is unclear whether and how estimation-uncertainty lingers to affect long-term decisions without opportunities to learn or to explore. Here, we show that sampling-rates acquired during a reinforcement learning phase (with feedback) correlate with decision biases in a subsequent test phase (without feedback), independently from outcome expectations. Further, computational model-fits to behavior are improved by estimation-uncertainty, and specifically so for options with smaller sampling-rates/larger estimation-uncertainties. These results are replicated in two additional independent datasets. Our findings highlight that estimation-uncertainty is an important factor to consider when trying to understand human decision making.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of experiencing the COVID-19 pandemic on optimistically biased belief updating.Elife. 2025 Jun 30;13:RP101157. doi: 10.7554/eLife.101157. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40587558 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptions and experiences of the prevention, detection, and management of postpartum haemorrhage: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 27;11(11):CD013795. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013795.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38009552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niv, Y. Reinforcement learning in the brain. J. Math. Psychol.53, 139–154 (2009).
-
- Seitz, A. & Watanabe, T. A unified model for perceptual learning. Trends Cognit. Sci.9, 329–334 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Doya, K. Complementary roles of basal ganglia and cerebellum in learning and motor control. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.10, 732–739 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Kaelbling, L. P., Littman, M. L. & Moore, A. W. Reinforcement learning: a survey. J. Artif. Intell. Res.4, 237–285 (1996).
-
- Botvinick, M. et al. Reinforcement learning, fast and slow. Trends Cognit. Sci.23, 408–422 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

