A longitudinal cohort study uncovers plasma protein biomarkers predating clinical onset and treatment response of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40691443
- PMCID: PMC12279936
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62032-1
A longitudinal cohort study uncovers plasma protein biomarkers predating clinical onset and treatment response of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
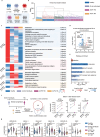
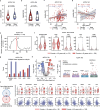
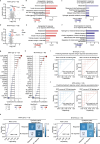
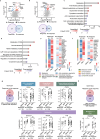
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic inflammatory condition posing challenges in identifying biomarkers for onset, severity and treatment responses. Here we investigate the plasma proteome in a longitudinal cohort of 278 RA patients, alongside 60 at-risk individuals and 99 healthy controls. We observe distinct proteome signatures in at-risk individuals and RA patients, with protein levels alterations correlating with disease activity, notably at DAS28-CRP thresholds of 3.1, 3.8 and 5.0. The combination of methotrexate (MTX) and leflunomide (LEF) modulates proinflammatory pathways, whereas MTX plus hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) impact energy metabolism. A machine-learning model is trained for predicting responses, and achieves average receiver operating characteristic (ROC) scores of 0.88 (MTX + LEF) and 0.82 (MTX + HCQ) in the testing sets. The efficiency of these models is further validated in independent cohorts using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay data. Overall, our study unveils distinct plasma proteome signatures across various stages and subtypes of RA, providing valuable biomarkers for predicting disease onset and treatment responses.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluating leflunomide and methotrexate combination vs. monotherapy in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis.Turk J Med Sci. 2025 Mar 24;55(3):632-643. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.6010. eCollection 2025. Turk J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40686714 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis naive to methotrexate: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 8;5(5):CD012657. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012657. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28481462 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid and folinic acid for reducing side effects in patients receiving methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 May 31;2013(5):CD000951. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000951.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23728635 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial lung diseases induced or exacerbated by DMARDS and biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014 Apr;43(5):613-26. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014. PMID: 24231065
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis unsuccessfully treated with biologics: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD012591. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012591. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28282491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smolen, J. S. et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis.82, 3–18 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Holmdahl, R., Malmström, V. & Burkhardt, H. Autoimmune priming, tissue attack and chronic inflammation - the three stages of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol.44, 1593–1599 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S., Boman, K., Tarkowski, A. & Hallmans, G. Up regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in anti-citrulline antibody and immunoglobulin M rheumatoid factor positive subjects precedes onset of inflammatory response and development of overt rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis.66, 121–123 (2007). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

