Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 at acidic pH is driven by partial unfolding of spike
- PMID: 40691508
- PMCID: PMC12280015
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08514-w
Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 at acidic pH is driven by partial unfolding of spike
Abstract
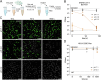
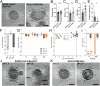
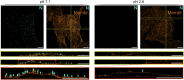
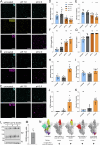
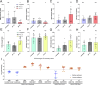
SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, is predominantly transmitted by respiratory aerosol and contaminated surfaces. Recent studies demonstrated that aerosols can become acidic, and acidification has been proposed as decontamination method. Here, we investigate how SARS-CoV-2 reacts to acidic pH and by which mechanism the virus is inactivated. We show that a pH below 3 is required to inactivate SARS-CoV-2 in a period of seconds to minutes. While we measured a 1000 to 10,000-fold drop in infectivity, virion structure remained intact under these conditions. Using super-resolution microscopy, we found that the attachment of virions to target cells is abrogated after acidic treatment, revealing spike protein (S) as the major inactivation target. Limited proteolysis of S combined with testing spike-specific antibodies for binding under low pH conditions revealed that exposure of SARS-CoV-2 to pH below 3 results in partial unfolding of S, thereby preventing binding of virions to target cells.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
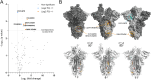
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO COVID-19 dashboard, accessed 19 June 2024 https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=o.
-
- Peacock, T. P. et al. The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is required for transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol.6, 899–909 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

