Effects of different modalities of combat sports on the motor skills of children and adolescents
- PMID: 40691569
- PMCID: PMC12281947
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-025-05814-2
Effects of different modalities of combat sports on the motor skills of children and adolescents
Abstract
Purpose: Motor skills are essential for carrying out daily tasks and the practice of physical activities can help to increase these skills. Being combat sports, it can be an alternative practice with this objective. However, it is not known which is the ideal modality. Therefore, the aim was to analyze the effects of nine months of practicing Muay Thai (MT) and Judo on the motor skills of children and adolescents.
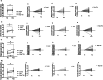
Methods: A sample of 109 young people from a Philanthropic Institution was distributed into: control (n = 36), Judo (n = 29) and MT (n = 44). The following motor skills tests were carried out: balance on the beam, side jumps, single-leg jump and transfer onto the platform. The intervention lasted nine months, twice a week for one hour.
Results: After nine months, the Judo and Muay Thai groups showed increased values in lateral jumps (Judo p-value < 0.001; Muay Thai p-value < 0.001), and transfer platform (Judo p-value = 0.007; Muay Thai p-value < 0.001) from the pre-moment compared to the post-moment. In the single-leg jump, the Judo (p-value = 0.011) and MT (p-value < 0.001) groups were different compared to the control group.
Conclusion: The practice of combat sports was effective in causing improvements in the motor skills of young.
Keywords: Adolescents; Children; Judo; Motor skills; Muay Thai.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This cross-sectional study was conducted in the city of Presidente Prudente, São Paulo, Brazil and was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the São Paulo State University-FCT/UNESP (CAAE: 26702414.0.0000.5402, Opinion number: 549.549, approved on March 7, 2014). The parents/legal guardians provided written consent. Lastly, the participants were recruited by convenience, and those who refused to participate were not included in this study. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Towards a Determination of the Physiological Characteristics Distinguishing Successful Mixed Martial Arts Athletes: A Systematic Review of Combat Sport Literature.Sports Med. 2016 Oct;46(10):1525-51. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0493-1. Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 26993133
-
Education support services for improving school engagement and academic performance of children and adolescents with a chronic health condition.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 8;2(2):CD011538. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011538.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36752365 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
What is the value of routinely testing full blood count, electrolytes and urea, and pulmonary function tests before elective surgery in patients with no apparent clinical indication and in subgroups of patients with common comorbidities: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effective literature.Health Technol Assess. 2012 Dec;16(50):i-xvi, 1-159. doi: 10.3310/hta16500. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 23302507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gallahue DL, Ozmun JC, Goodway JD, de Sales DR, Petersen RDS. Compreendendo o desenvolvimento motor – bebês, crianças, adolescentes e adultos., 7th ed., 2013.
-
- Abrams TC, Terlizzi BM, De Meester A, Sacko RS, Irwin JM, Luz C, Rodrigues LP, Cordovil R, Lopes VP, Schneider K, Stodden DF. Potential relevance of a motor skill proficiency barrier on health-related fitness in youth. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023;23:1771–8. 10.1080/17461391.2022.2153300. - PubMed
-
- Lopes LO, Lopes VP, Santos R, Pereira B. Associações entre actividade física, habilidades e coordenação Motora Em Crianças Portuguesas. Revista Brasileira De Cineantropometria E Desempenho Humano. 2010;15–21. 10.5007/1980-0037.2011v13n1p15.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

