Metal-organic nanostructures based on sono/chemo-nanodynamic synergy of TixOy/Ru reaction units: for ultrasound-induced dynamic cancer therapy
- PMID: 40691611
- PMCID: PMC12281788
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03599-1
Metal-organic nanostructures based on sono/chemo-nanodynamic synergy of TixOy/Ru reaction units: for ultrasound-induced dynamic cancer therapy
Abstract
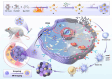
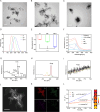
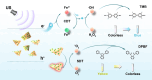
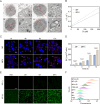
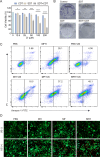
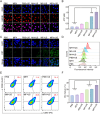
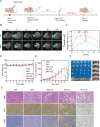
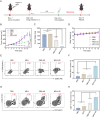
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) exhibits clinical potential for deep-tissue tumor treatment due to its deep tissue penetration and spatiotemporal controllability. Its core mechanism relies on ultrasound-activated sonosensitizers to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby inducing tumor cell apoptosis. However, conventional sonosensitizers face limitations in ROS yield and tumor-targeting efficiency. In this study, we innovatively designed a multifunctional metal-organic nanosheet (TiZrRu-MON) by hydrothermal coordination of [Ru(bpy)₃]2⁺ photosensitizing units with TiZr-O clusters, while incorporating Fe3⁺ to construct a cascade catalytic system. Experimental results demonstrated that: (1) Fe3⁺ lattice doping significantly enhanced charge carrier mobility and ultrasound-triggered 1O₂ quantum yield via the formation charge transfer channels; (2) The acidic tumor microenvironment activated Fe3⁺-mediated Fenton reactions, establishing a positive feedback loop with SDT to synergistically amplify ROS generation; (3) Hyaluronic acid functionalization improved nanosheet internalization in HepG2 tumor cells through CD44 receptor-mediated endocytosis. Remarkably, ultrasound irradiation induced substantial oxidative stress and immunogenic cell death, promoting the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which elevated the maturation rate of tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells (DCs) and significantly increased the proportion of CD8⁺ T cells. In a mouse subcutaneous tumor model, the system achieved effective tumor suppression with manageable systemic toxicity. This work proposes a metal-ligand coordination strategy to advance the development of high-performance sonosensitizers and immunomodulatory antitumor technologies.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Chemodynamic therapy; Magnetic resonance imaging; Metal–organic nanostructure; Sonodynamic therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All the animals were raised at Animal Care and Use Committee of Xiamen University (Ethics number XMULAC20190146). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Raju GSR, Dariya B, Mungamuri SK, Chalikonda G, Kang SM, Khan IN, et al. Nanomaterials multifunctional behavior for enlightened cancer therapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;69:178–89. - PubMed
-
- Cheng P, Ming S, Cao W, Wu J, Tian Q, Zhu J, et al. Recent advances in sonodynamic therapy strategies for pancreatic cancer. Wiley Interdiscipl Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024;16(1): e1945. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82302403/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2024HR03/Sichuan Provincial Health Commission special research project
- 2024JDKP0022/Sichuan Science and Technology Department Science and Technology Ability Improvement Project
- 23JCYJPT0043/Nanchong Science and Technology Bureau Basic Research Platform Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

