Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the GRAS gene family in Medicago lupulina L
- PMID: 40691755
- PMCID: PMC12278555
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11855-9
Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the GRAS gene family in Medicago lupulina L
Abstract
Background: Transcription factors encoded by GRAS genes play pivotal roles in a wide range of biological processes, including signal transduction, plant growth and development, and responses to various abiotic and biotic stresses. Nevertheless, to date, the GRAS gene family has not been previously identified or analyzed in Medicago lupulina L.
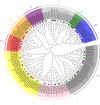
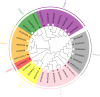
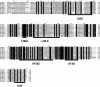
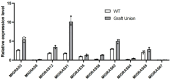
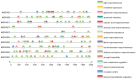
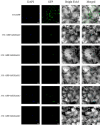
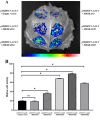
Results: In this study, bioinformatic approaches were used to analyze genomic data of M. lupulina obtained from our laboratory, resulting in the identification of 52 GRAS genes (designated as MlGRASs). We predicted and analyzed the physicochemical properties, subcellular localization, protein structures, phylogenetic relationships, gene structures, and sequence characteristics of these genes. Phylogenetic analysis showed that 52 MlGRASs were categorized into eight different subfamilies: LILIUM LONGIFLORUM SCR-LIKE (LISCL), SHORT ROOT (SHR), PHYTOCHROME A SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION 1 (PAT1), SCARECROW-LIKE 3 (SCL3), DELLA, HAIRY MERISTEM (HAM), LATERAL SUPPRESSOR (LS) and SCARECROW (SCR). Notably, we identified 10 M. lupulina GRAS genes belonging to the PAT1 subfamily. Experimental results from RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that MlPAT1s genes were expressed in leaves, stems and roots of M. lupulina. Moreover, in the graft union, the expression levels of most MlPAT1s were higher than those in the wild type M. lupulina. To further predict the potential functions of MlPAT1s genes, we performed molecular cloning and transcriptional activation assays on MlGRAS3/31/35/62/65. The transcriptional activation assay revealed that 35 S:GFP-MlGRAS31/35/62/65 positively regulated the expression of MlDOF3.4, a gene implicated in cell proliferation and regeneration.
Conclusions: This study provided a theoretical framework for further investigation into the roles of PAT1 proteins in M. lupulina.
Keywords: GRAS gene; Medicago lupulina L; PAT1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRAS gene family and their expression profiles under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses in Amorphophallus konjac.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 8;26(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11777-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40629278 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of nine PAT1 genes subfamily in Medicago edgeworthii.Plant Signal Behav. 2025 Dec;20(1):2527380. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2025.2527380. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2025. PMID: 40592482 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the GRAS code: evolutionary phylogeny and functional diversification of a key gene family in Populus simonii.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):816. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06828-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40604419 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analysis of the Seven IN Absentia (SINA) genes in bread wheat sheds light on their structure in plants.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 21;18(12):e0295021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295021. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38127955 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Pysh LD, Wysocka-Diller JW, Camilleri C, Bouchez D, Benfey PN. The GRAS gene family in Arabidopsis: sequence characterization and basic expression analysis of the SCARECROW-LIKE genes. Plant J. 1999;18(1):111–9. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Widmer A. Genome-wide comparative analysis of the GRAS gene family in Populus, Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biology Report. 2014;32(6):1129–45.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

