Comparative Analysis of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Protein Extraction Methodologies for Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 40691760
- PMCID: PMC12323001
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5c00089
Comparative Analysis of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Protein Extraction Methodologies for Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
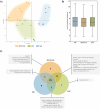
The aim of this study is to present a comparative study of different methodologies for the extraction of proteins from platelet-derived extracellular vesicles (pEVs) prior to subsequent mass spectrometry (MS) analysis. pEVs were isolated by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) from human platelet lysates (PL) and characterized by identifying specific markers by Western blot, visualizing morphology by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and analyzing concentration and size via nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). Protein isolation was performed through three different methodologies based on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), organic solvent precipitation (OSP), or magnetic beads (MB), followed by protein digestion and sample acquisition by LC-MS/MS. Clustering of the samples according to methodology is observed in the principal component analysis (PCA), although no significant differences in terms of normalized abundances are reached. Similarly, a small number of proteins were identified as unique by each methodology, with 91.3% coincidence among all three procedures. In addition, the bioinformatic results of the enrichment analysis and the numbers of proteins already identified in the Vesiclepedia database are highly similar for the three methodologies. Overall, all three methodologies analyzed are optimal for the extraction of proteins from pEV and could be considered according to their intrinsic characteristics, in accordance with the research requirements.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; mass spectrometry; methodologies; platelets; proteins; proteomics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Multiomic Study of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Impact of Platelet Concentrate Sources.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2025 Aug 19;2025:8358424. doi: 10.1049/nbt2/8358424. eCollection 2025. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40873929 Free PMC article.
-
The proteome of circulating extracellular vesicles and their functional effect on platelets vary with the isolation method.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05374-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594329 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the Soluble and Extracellular Vesicle Protein Compartments of Plasma Using In-Depth Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics.J Proteome Res. 2024 Sep 6;23(9):4114-4127. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00490. Epub 2024 Aug 14. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 39141927 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Pathogen-reduced platelets for the prevention of bleeding.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 30;7(7):CD009072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009072.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28756627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cufaro M. C., Pieragostino D., Lanuti P., Rossi C., Cicalini I., Federici L., De Laurenzi V., Del Boccio P.. Extracellular Vesicles and Their Potential Use in Monitoring Cancer Progression and Therapy: The Contribution of Proteomics. J. Oncol. 2019;2019:1. doi: 10.1155/2019/1639854. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mallia A., Gianazza E., Zoanni B., Brioschi M., Barbieri S. S., Banfi C.. Proteomics of Extracellular Vesicles: Update on Their Composition, Biological Roles and Potential Use as Diagnostic Tools in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Diagnostics. 2020;10(10):843. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100843. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yáñez-Mó M., Siljander P. R.-M., Andreu Z., Bedina Zavec A., Borràs F. E., Buzas E. I., Buzas K., Casal E., Cappello F., Carvalho J., Colás E., Cordeiro-da Silva A., Fais S., Falcon-Perez J. M., Ghobrial I. M., Giebel B., Gimona M., Graner M., Gursel I., Gursel M., Heegaard N. H. H., Hendrix A., Kierulf P., Kokubun K., Kosanovic M., Kralj-Iglic V., Krämer-Albers E., Laitinen S., Lässer C., Lener T., Ligeti E., Line̅ A., Lipps G., Llorente A., Lötvall J., Manček-Keber M., Marcilla A., Mittelbrunn M., Nazarenko I., Nolte-‘t Hoen E. N. M., Nyman T. A., O’Driscoll L., Olivan M., Oliveira C., Pállinger É., Del Portillo H. A., Reventós J., Rigau M., Rohde E., Sammar M., Sánchez-Madrid F., Santarém N., Schallmoser K., Stampe Ostenfeld M., Stoorvogel W., Stukelj R., Van Der Grein S. G., Helena Vasconcelos M., Wauben M. H. M., De Wever O.. Biological Properties of Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2015;4(1):27066. doi: 10.3402/JEV.V4.27066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

