Xist condensates: perspectives for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 40691806
- PMCID: PMC12278583
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-025-03666-8
Xist condensates: perspectives for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
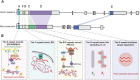
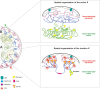
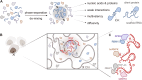
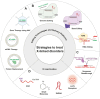
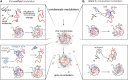
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a crucial mechanism of dosage compensation in female mammals ensuring that genes from only one X chromosome are expressed, initiated through expression of the long noncoding RNA Xist. Recent evidence underscores the significance of molecular crowding-most likely via liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS)-in forming Xist RNA-driven condensates critical for establishing and sustaining the silenced state. By integrating existing knowledge and emerging ideas, we provide a comprehensive perspective on the molecular underpinnings of XCI and outline how manipulation of LLPS-based mechanisms offers new avenues for novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Condensate-modifying therapeutics; Condensates; Liquid-liquid phase separation; RNA-binding proteins; X-chromosome inactivation; X-linked disorders; X-reactivation; Xist.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval was not applicable. Competing interests: A.C. and G.G.T. are co-founder of CERNAIS®. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Heard E. Recent advances in X-chromosome inactivation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:247–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

