The value of ultrasonographic scoring method and nomogram in assessing cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 40691855
- PMCID: PMC12281816
- DOI: 10.1186/s13044-025-00255-6
The value of ultrasonographic scoring method and nomogram in assessing cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
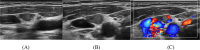
Background: The preoperative cervical lymph node metastasis (CLNM) status in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) critically determines the type of lymph node dissection performed. Currently, ultrasonography is the primary method for initial CLNM screening in PTC patients. This study aims to analyze the efficacy of an ultrasonic-characteristics-based scoring system in diagnosing lymph node metastasis in PTC and construct a predictive nomogram.
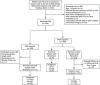
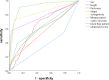
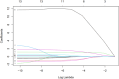
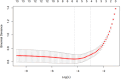
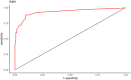
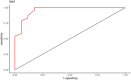
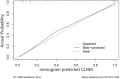
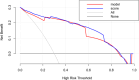
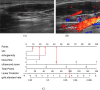
Methods: The imaging findings, fine-needle aspiration (FNA) results, and surgical pathology data from 269 suspected CLNM cases at Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, spanning from July 2021 to October 2022, were retrospectively analyzed. We identified specific ultrasound characteristics and assigned scores based on our clinical experience. The diagnostic performance of the ultrasound scoring system was assessed by plotting receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and calculating the area under the curve (AUC). Additionally, a nomogram was developed using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-logistic regression. The nomogram's discrimination was evaluated using ROC analysis, its accuracy was assessed with calibration curves, and its clinical utility was determined by decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: In this study, factors such as age, sex, lymph node length, thickness, aspect ratio, shape, hilum status, echogenicity, microcalcification, cystic necrosis, blood flow pattern, and the ultrasonic score were included in the analysis. The ultrasound score had the highest (AUC = 0.914, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.880-0.950), with an optimal cutoff value of 2.5. A score of 3 or higher had a diagnostic sensitivity for CLNM of 81.1%, specificity of 85.2%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 83.1%, negative predictive value (NPV) of 83.4%, and Kappa value of 0.664. Subsequent LASSO regression analysis identified sex, hyperechogenicity, peripheral disordered blood flow, and the ultrasonic score as independent predictors of CLNM, which were incorporated into a logistic regression-based predictive nomogram. The model exhibited strong discriminatory performance in both the training set (AUC = 0.933, 95% CI: 0.820-0.910) and the test set (AUC = 0.958, 95% CI: 0.790-0.890) for distinguishing PTC with and without CLNM. Furthermore, calibration curves and decision curve analysis (DCA) confirmed the model's good fit and favorable clinical net benefit.
Conclusion: The ultrasonic scoring method and the Nomogram have significant clinical utility in the preoperative assessment of CLNM in PTC, reducing unnecessary FNA procedures, and are simple and practical for clinical application.
Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Keywords: Cervical lymph node metastasis(CLNM); Nomogram; Papillary thyroid carcinoma(PTC); Ultrasonography.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Human ethics and consent to participate declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital (Approval No.: Peking University Shenzhen Medical Ethics (Research) [2024] No. (015). Published written informed consent was obtained from patients and/or their legal guardians. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lu KN, Zhang Y, Da JY, et al. A novel scoring system for predicting the metastases of posterior right recurrent laryngeal nerve lymph node involvement in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma by preoperative ultrasound. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:738138. 10.3389/fendo.2021.738138. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

