Gut Microbiota Mediate Periampullary Cancer Through Extracellular Matrix Proteins: A Causal Relationship Study
- PMID: 40692118
- PMCID: PMC12279554
- DOI: 10.1049/syb2.70027
Gut Microbiota Mediate Periampullary Cancer Through Extracellular Matrix Proteins: A Causal Relationship Study
Abstract
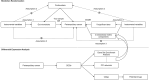
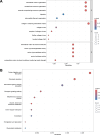
Recent studies have reported that gut microbiota may play a role in the occurrence and development of digestive system cancers. Periampullary cancer is a relatively rare digestive system cancer which lacks effective targeted therapy and specific drugs. The purpose of this study is to elucidate the relationship between periampullary cancer and gut microbiota. This work collected public genome-wide association study (GWAS) data from 211 gut microbial taxa and three types of cancer related to periampullary cancer, which were used for two-sample Mendelian randomisation (MR) analysis. Based on the analysis of differentially expressed genes between periampullary cancer and adjacent normal tissue, extracellular matrix proteins were selected for further multivariable MR analysis. Finally, the Connectivity Map was used to screen potential therapeutic drugs for periampullary cancer. Two-sample MR results confirmed that nine microbial taxa, Tyzzerella, Alloprevotella, Holdemania, LachnospiraceaeUCG010, Terrisporobacter, Alistipes, Rikenellaceae, Anaerofilum and Dialister, were associated with periampullary cancer risk. Multivariable MR discovered extracellular matrix-related proteins [Collagen alpha-1(I) chain, Laminin, Fibronectin and Mucin] that may play a role in the association between gut microbiota and periampullary cancer. Finally, the Connectivity Map identified 27 potential candidate drugs. This study can provide theoretical basis for future prevention and diagnostic research on this rare cancer.
Keywords: bioinformatics; cancer; microorganisms.
© 2025 The Author(s). IET Systems Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Institution of Engineering and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammatory cytokines mediate the gut microbiota-EGPA subtype link: a Mendelian randomization study.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;44(7):3061-3071. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07526-5. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40500572
-
Exploring the role of gut microbiota in intervertebral disc degeneration: insights from bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis.Eur Spine J. 2025 Jun;34(6):2092-2105. doi: 10.1007/s00586-025-08794-0. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Eur Spine J. 2025. PMID: 40257470
-
Gut microbiota causally affects ulcerative colitis by potential mediation of plasma metabolites: A Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 27;104(26):e42791. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042791. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40587710 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiome-based interventions for the management of obesity in children and adolescents aged up to 19 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jul 10;7(7):CD015875. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015875. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40637175 Review.
References
-
- Hester C. A., Dogeas E., Augustine M. M., et al., “Incidence and Comparative Outcomes of Periampullary Cancer: A Population‐Based Analysis Demonstrating Improved Outcomes and Increased Use of Adjuvant Therapy From 2004 to 2012,” Journal of Surgical Oncology 119, no. 3 (2018): 303–317, 10.1002/jso.25336. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 24ZDFA001/Gansu Provincial Science and Technology Major Project
- 2024-4-2/Lanzhou Municipal Science and Technology Program
- 2025-2-100/Lanzhou Municipal Science and Technology Program
- 2025-2-103/Lanzhou Municipal Science and Technology Program
- 20250260006/College Students' Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Lanzhou University, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

